What is SEO? Learn Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Updated:

Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a key component of any digital marketing strategy. It involves optimizing a website to improve its visibility on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo!. By enhancing website visibility and driving organic traffic, SEO helps businesses achieve higher search engine rankings and ultimately increase revenue.
Search engines act as digital libraries, constantly discovering, crawling, indexing, and serving search results to users. SEO helps businesses appease search engines by providing high-quality, optimized, and relevant content that aligns with their algorithms.
SEO encompasses various types, including on-page SEO optimization, off-page SEO optimization, and technical SEO. Each type focuses on different aspects of website optimization, from content and keywords to site architecture and website codebase.
Understanding search engines, implementing a comprehensive SEO strategy, and utilizing the right tools are key to staying competitive in the online landscape, driving targeted traffic, and achieving business objectives.
Table of Contents
What Is SEO?
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is a process that involves optimizing the website to improve its visibility on Google, Bing, Yahoo!, and other major search engines.
SEO enhances website visibility, driving higher organic traffic through improved search engine ranking. It ensures a prominent search engine results page (SERP) placement when users search for relevant phrases related to your products, services, or expertise.
Increased website visibility boosts the likelihood of attracting clicks and visitors to your web page. SEO serves as a valuable tool for businesses and website owners, driving higher website traffic and ultimately leading to increased revenue.
Why Is SEO Important?
SEO is a critical component of any digital marketing strategy.
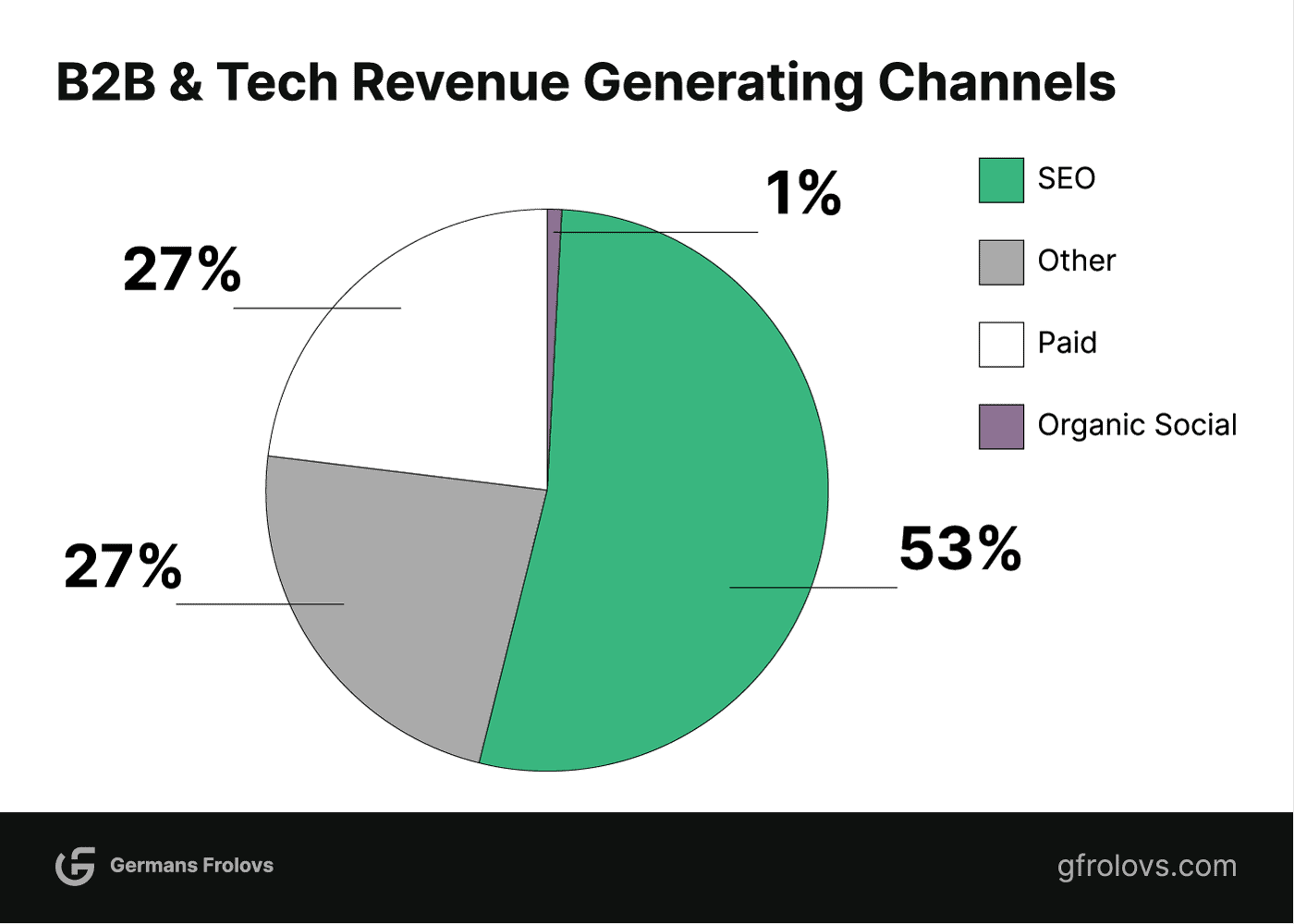
Organic search traffic, responsible for 53% of all website traffic according to a BrightEdge Research study conducted in May 2019, showcases the significant role it plays in driving website visits. The study sourced data from thousands of domains and tens of billions of sessions to develop these findings.

B2B and technology companies generate up to 2 times more revenue, accounting for 53%, from organic search compared to other channels.
The global SEO services market size is forecasted to reach USD 234.8 Billion by 2030, as stated in the report titled “Search Engine Optimization Services Market Forecast, 2022 – 2030” by Acumen Research and Consulting.
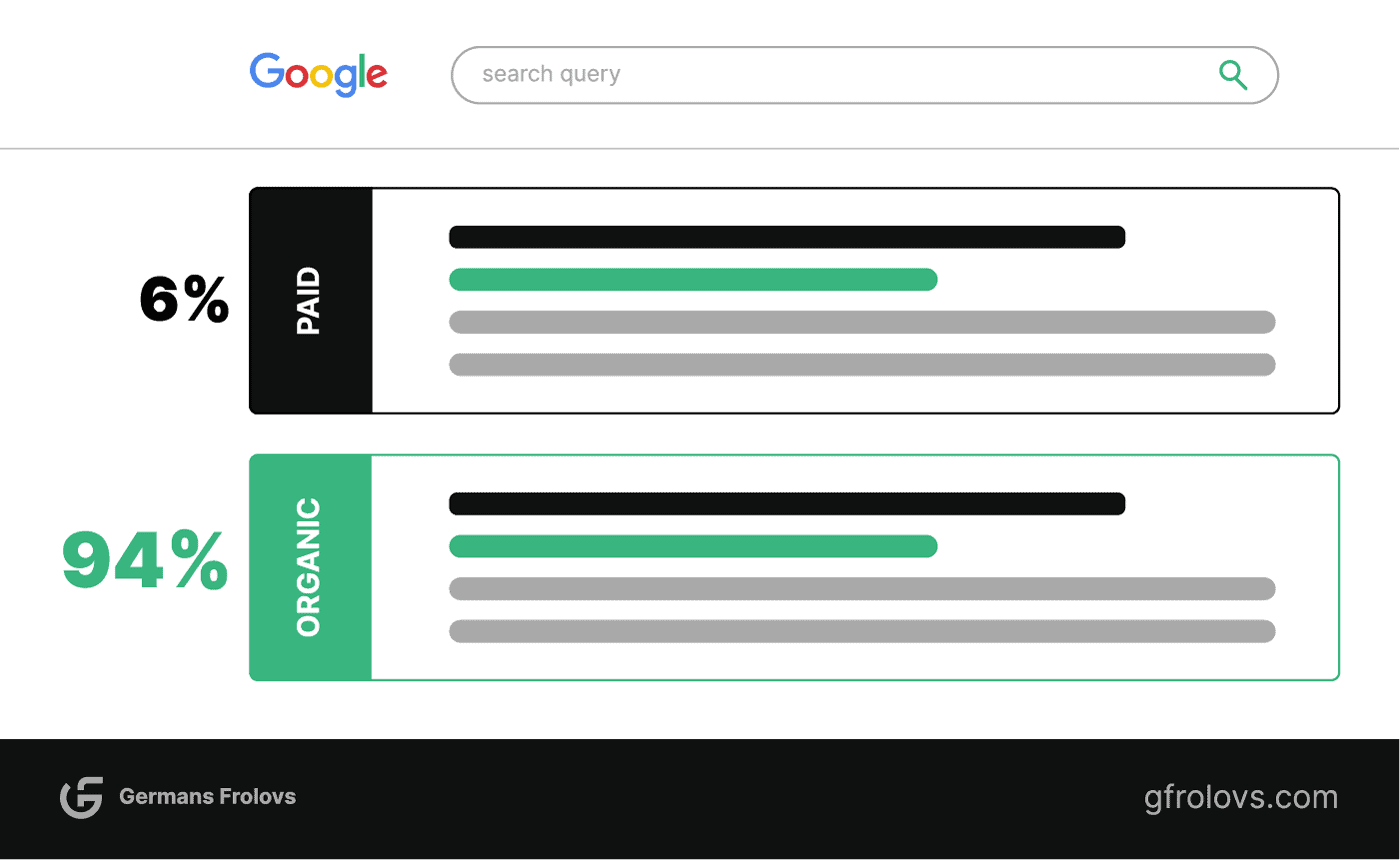
94% of people using search engines such as Google and Bing click on organic results rather than sponsored ads, as revealed by research conducted by GroupM UK and Nielsen. This data is based on a sample of 28 million UK citizens and 1.4 billion searches conducted in June 2011.
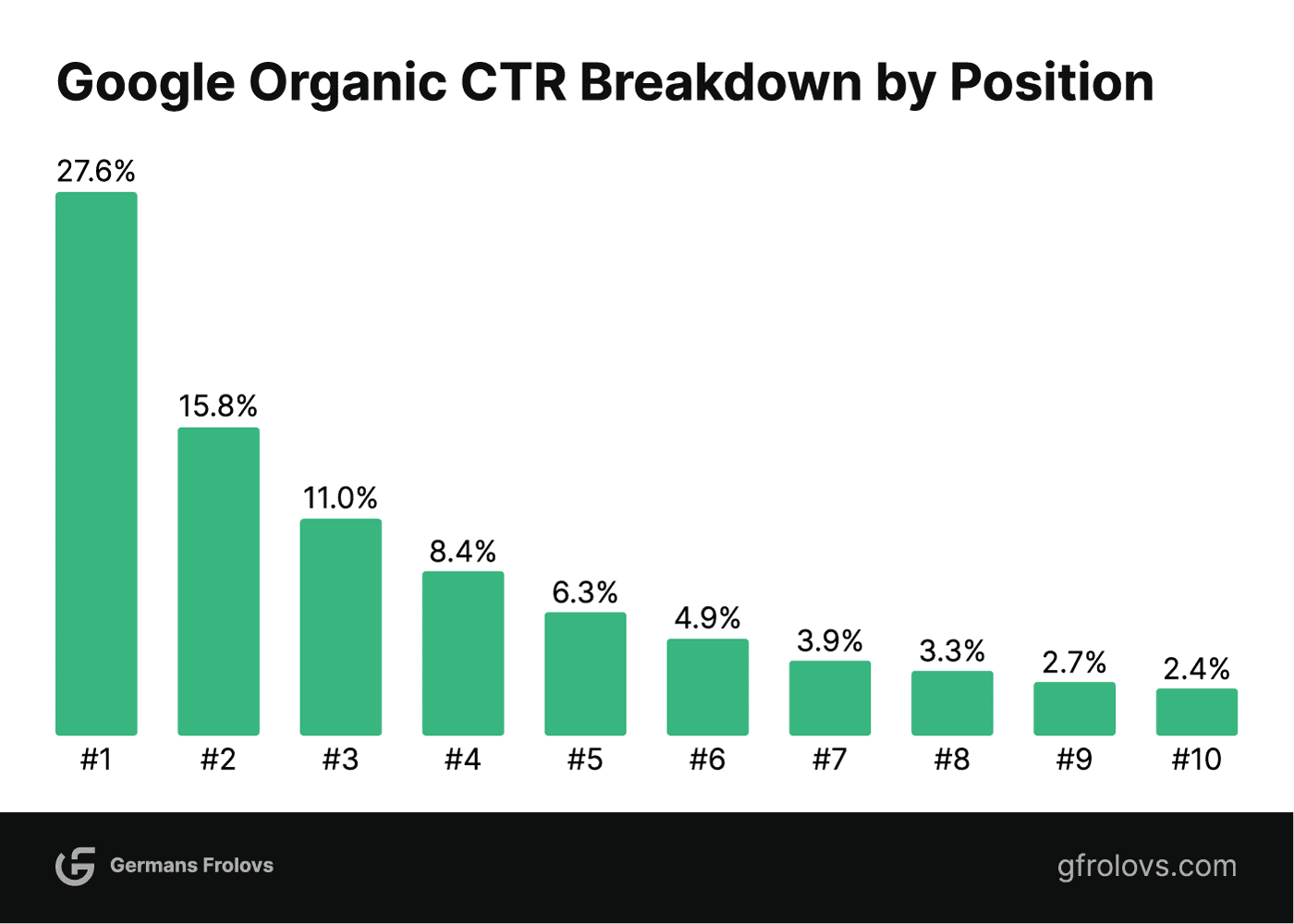
The number 1 organic result in Google gets 27.6% of all clicks, which is almost 10 times higher than the results in positions 8-10, as revealed by a study conducted by Brian Dean from Backlinko and Semrush in 2022.
The statistics clearly demonstrate that SEO is a crucial digital marketing channel that generates substantial business results and growth for companies of all sizes. By improving online visibility, SEO should be treated with utmost seriousness.
Other reasons why SEO is important for businesses are the following.
- Increasing online visibility and brand perception: SEO boosts online presence and credibility, attracting potential customers by positioning websites as trustworthy and authoritative.
- Targeting high-quality traffic: SEO allows targeting users specifically searching for a business’s products or services, making it a cost-effective marketing channel that captures high-quality traffic.
- Enhancing user experience: SEO improves website navigation, loading times, and mobile-friendliness, leading to greater user engagement and higher conversion rates.
- Providing continuous and long-term benefits: Well-optimized websites enjoy lasting high rankings, making SEO a cost-effective, long-term investment for maintaining an online presence and driving growth.
Neglecting SEO and not knowing how search engines work could cause businesses to miss out on potential clients and revenue. Investing in SEO should be a priority for any business that wants to stay competitive online.
How Do Search Engines Work?
In simple terms, search engines work like digital libraries for the modern age.
They serve as extensive repositories of information, easily accessible to users through a user-friendly interface. Users can swiftly and efficiently find the information they require.
This is achieved by discovering, crawling, indexing, and serving results using a complex yet streamlined web of algorithms and processes.
The overall process is much more complex but at a basic level, it can be broken down into four main stages.
- Discovering: The first step in the search engine process is to discover new websites and web pages. This can be accomplished through manual submissions, sitemaps, and following links from other websites. In essence, search engines work like explorers, constantly seeking new content to add to their digital library.
Library example: In a library setting, the first step involves discovering new books and resources for the collection through recommendations, catalogs, and references. Librarians continuously discover new content to enrich their libraries.
- Crawling. Once a new website or web page has been discovered, search engines deploy web crawlers or spiders to gather data and information about the content. The spiders follow links within the website and across different websites, creating a vast network of interconnected pages. This process also involves examining aspects of websites, such as meta tags, headers, and textual content.
Library example: The crawling process can be compared to flipping through the pages of a book or scanning a book’s barcode, allowing the librarian to catalog it accordingly.
- Indexing: After gathering the data, search engines organize and store the information in an easily searchable format. This process is referred to as indexing. Indexing involves processing the data collected by the web crawlers, analyzing factors such as keywords, website structure, and content quality, and then storing it in a database.
Library example: Indexing is similar to a librarian cataloging and shelving books in a library, ensuring they are easily accessible when needed.
- Serving search results: The final step in the search engine process is delivering relevant search results to users in an organized manner. When a user types in a query, the search engine refers to its index and retrieves the most appropriate web pages, and ranks them in SERPs based on various factors, such as relevance, quality, and user interaction.
Library example: In a library setting, this would be like the librarian providing you with a list of books on your chosen subject, ranked by their relevance.
The importance of the last step cannot be understated as it ensures users get exactly what search engines want them to – the most relevant and useful results.

What Do Search Engines Want?
Search engines want to provide the best possible search experience to the users.
This means delivering the most relevant and accurate results as quickly as possible so that users can find the information they need and are satisfied with the outcome.
Understanding and meeting the goals of search engines is crucial for website owners to ensure favorable rankings in SERPs and attract organic traffic. To achieve this, it is imperative to furnish search engines with quality content that is well-structured, relevant, and optimized for their algorithms.
By doing so, the cost of not featuring your website’s content becomes higher than the cost of featuring it, prompting search engines to rank it highly.
As you seek to appease the true desires of search engines like Google and your site users, it’s essential to understand why SEO focuses so much on Google in particular.
Why SEO Focuses So Much On Google?
SEO focuses so much on Google primarily due to its dominance in the search engine market.
Google accounted for 86.84% percent of the global desktop search market, as of April 2023, according to StatCounter.
Many people associate the phrase “search engine” with Google, even to the point when people start to use it as a verb (e.g. “googling”). So naturally, SEO professionals have to prioritize optimizing for the search engine giant.
Google also provides a wide variety of tools, to help SEO professionals analyze and improve their content.
From its PageSpeed Insights (PSI) tool which reports on the user experience of a page and provides suggestions on how that page may be improved to Google Search Console (GSC) which helps measure a site’s search traffic and performance, diagnose and fix SEO issues, to many other SEO tools, Google provides a comprehensive suite of tools to help website owners optimize their website.
Google continually refines its search algorithms and transforms the presentation of its SERPs to prioritize user experience and deliver personalized search results. As a result, SEO professionals must remain proactive in adapting their content to align with Google’s ever-evolving guidelines. It is crucial to stay ahead of the curve and optimize content to meet the demands of Google’s dynamic search landscape.
For example, Google has introduced a new experiment in Search Labs called SGE (Search Generative Experience), currently available in the U.S. (English-only at launch), which was launched in May 2023.
What is The Anatomy of Search Results?
SERPs consist of various components, primarily sponsored and organic listings.
The composition of these listings varies based on factors such as the nature of the search query, the intent of the searcher, and the level of competition among advertisers.
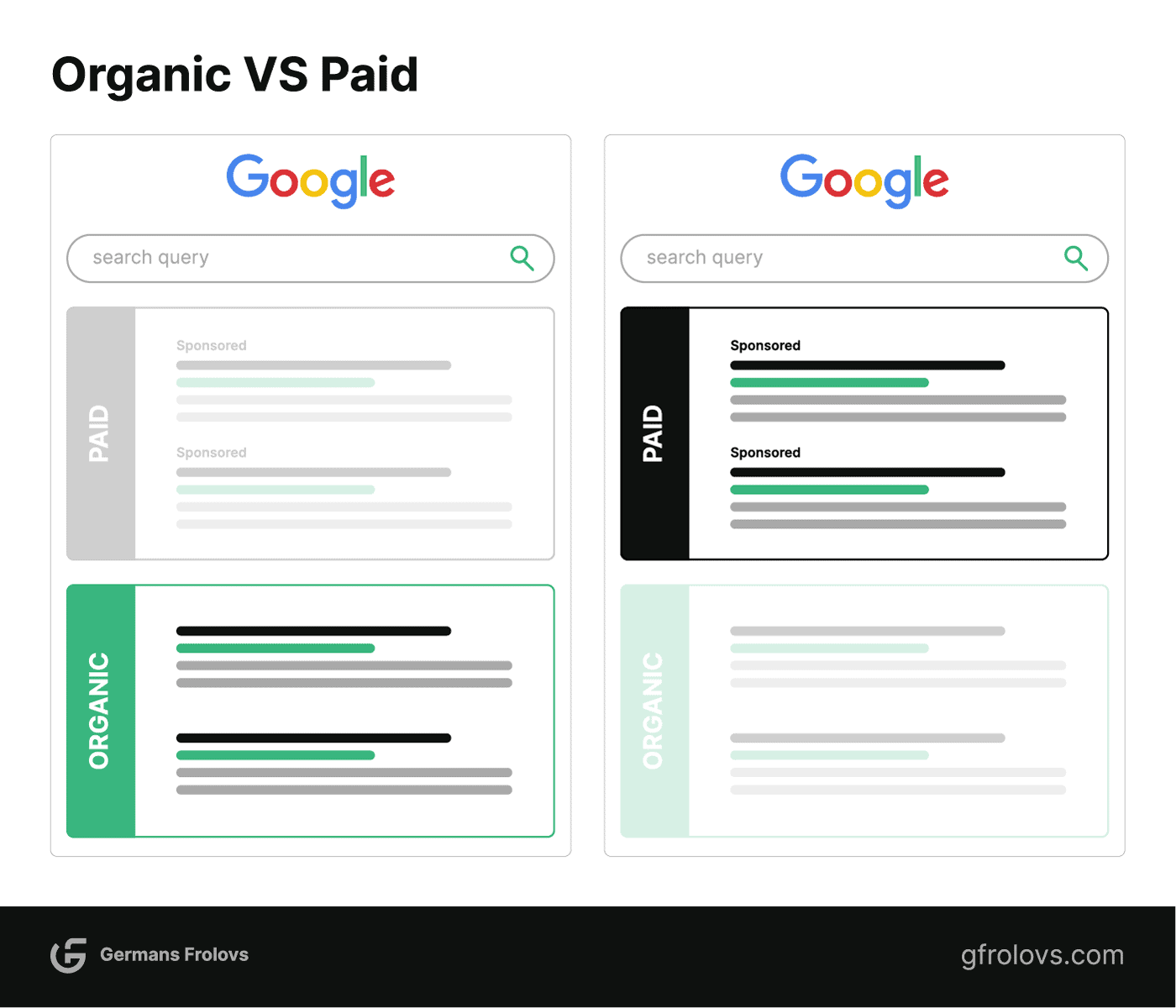
What Are Sponsored Listings?
The sponsored listings on a SERP refer to the paid advertisements that appear at the top and bottom of the search results. These listings are usually marked with an “Ad” or “Sponsored” label (Google is known for testing it from time to time) and are displayed in response to specific keyword searches.
The number of sponsored listings on a SERP depends on the popularity of the keywords and the level of competition among advertisers.
In highly competitive industries, where multiple advertisers compete for the same keywords, it is common to observe a higher number of sponsored results within SERPs, up to a certain limit. Additionally, the intensified competition often leads to higher costs-per-click (CPC), as advertisers are willing to invest more to secure prominent ad placements and visibility in search results.
Advertisers use advertising channels like Google Ads to bid on specific keywords, and their visibility or “impression share” in the search results is determined by factors such as the bid amount, quality score, and ad relevance.
Sponsored listings allow businesses to increase visibility and reach potential customers faster than organic listings, but they require continuous investment to maintain their presence on SERPs.
What Are Organic Listings?
Organic listings are the non-paid search results that appear on the SERP.
Google and other search engines use sophisticated algorithms to evaluate and rank websites, considering various ranking factors such as content quality, backlinks, and many other ranking factors.
Organic listings are essential for businesses and website owners, as they provide long-term visibility and gradually increase traffic without requiring continuous investment like sponsored listings.
Achieving higher organic rankings is the primary goal of SEO efforts and leads to increased credibility, customer trust, and better return on investment (ROI).
What Are The Different SERP Elements Depending on Query Type?
Google and other search engines strive to provide the most relevant and useful results for each query, adapting the SERP’s layout and components based on the searcher’s intent and the nature of the query.
Below is a list of the most common elements that appear on a SERP based on the query type.
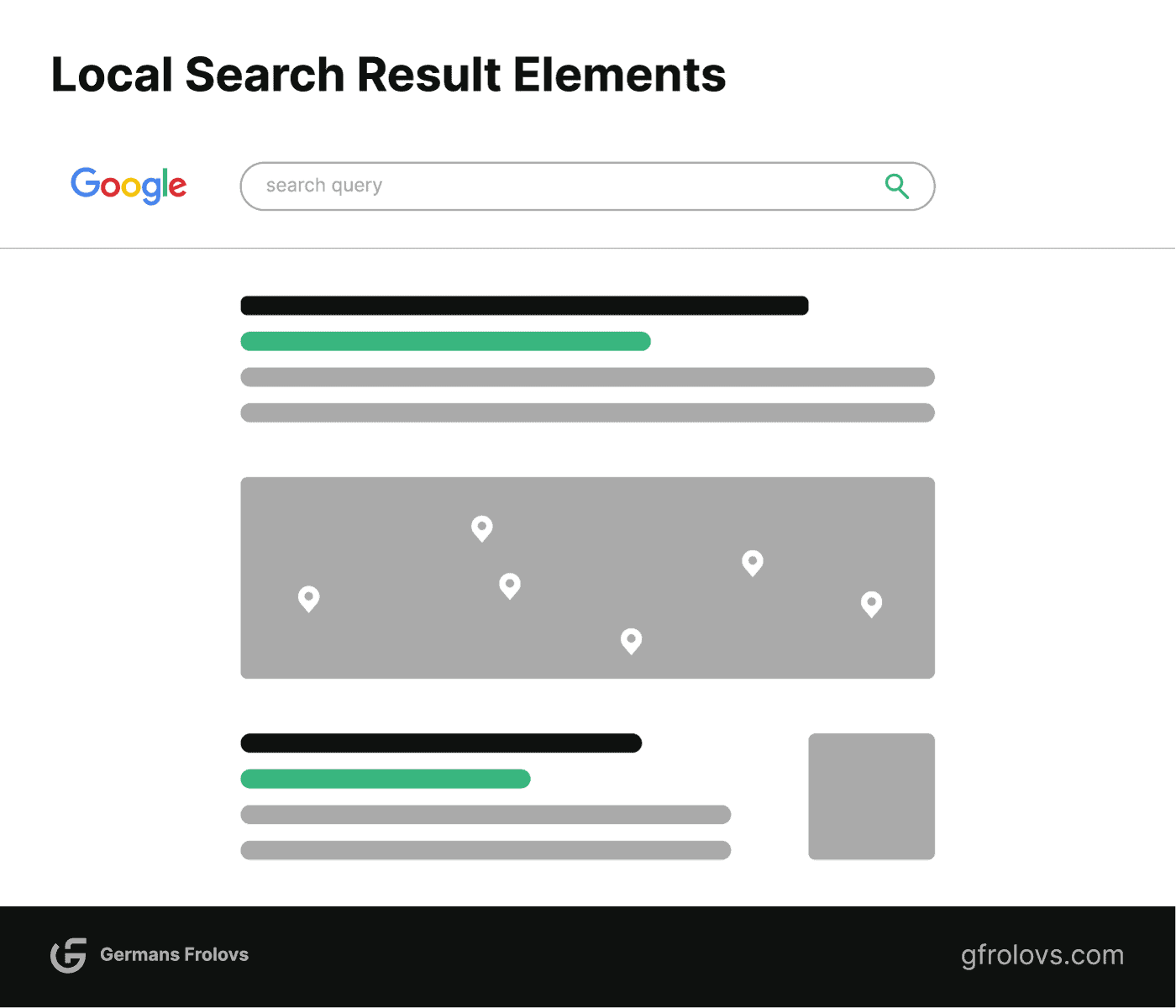
Local Searches
Search queries that indicate a local intent, such as “coffee shop near me,” often trigger the inclusion of a Google Maps snippet within the SERP. This snippet showcases the nearest business locations along with relevant details such as ratings, addresses, and phone numbers.
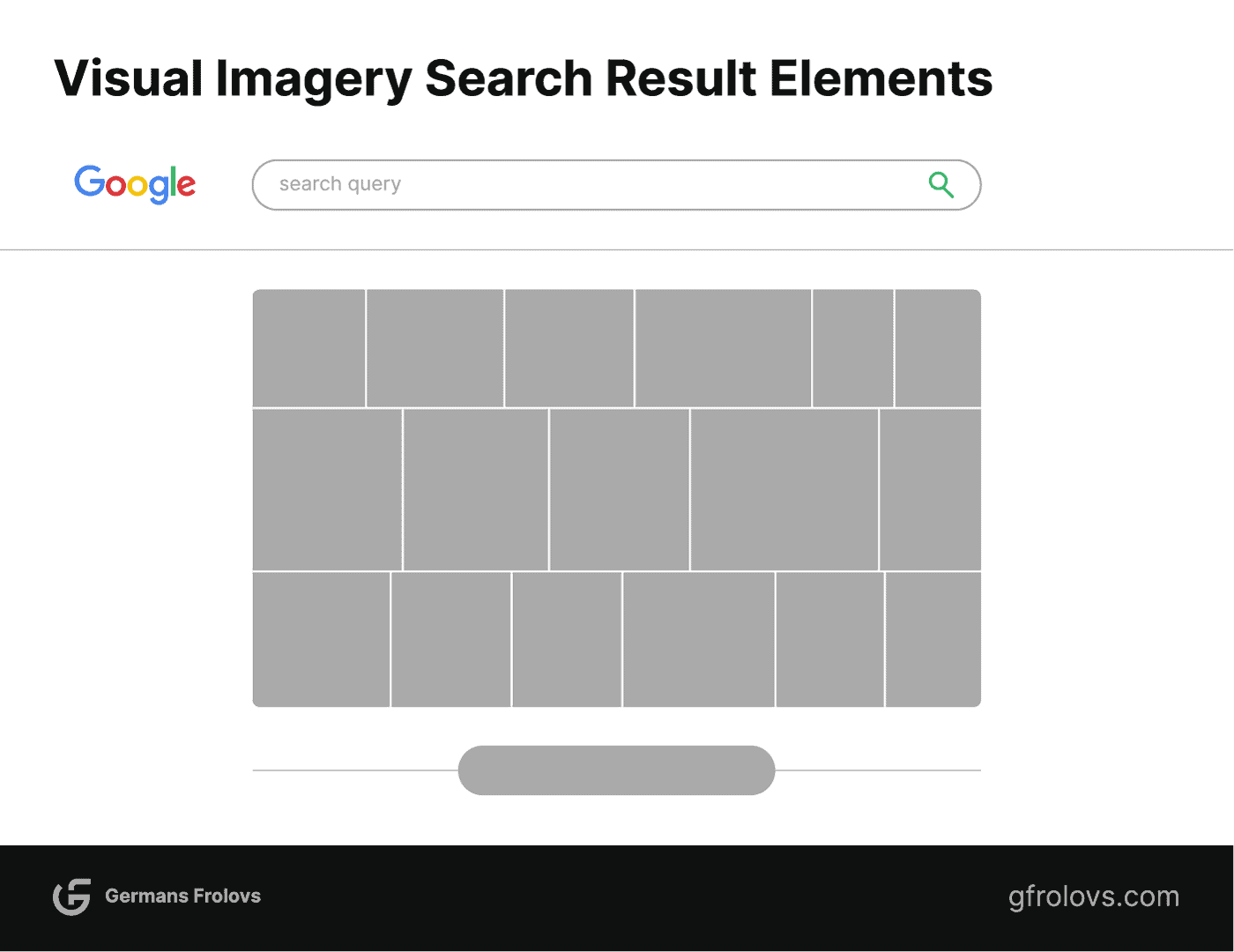
Visual Imagery Searches
When users search for queries that may require visual representations, such as “home interior design ideas,” the SERP may prominently display an image carousel. This carousel showcases a collection of related images sourced from various sites.
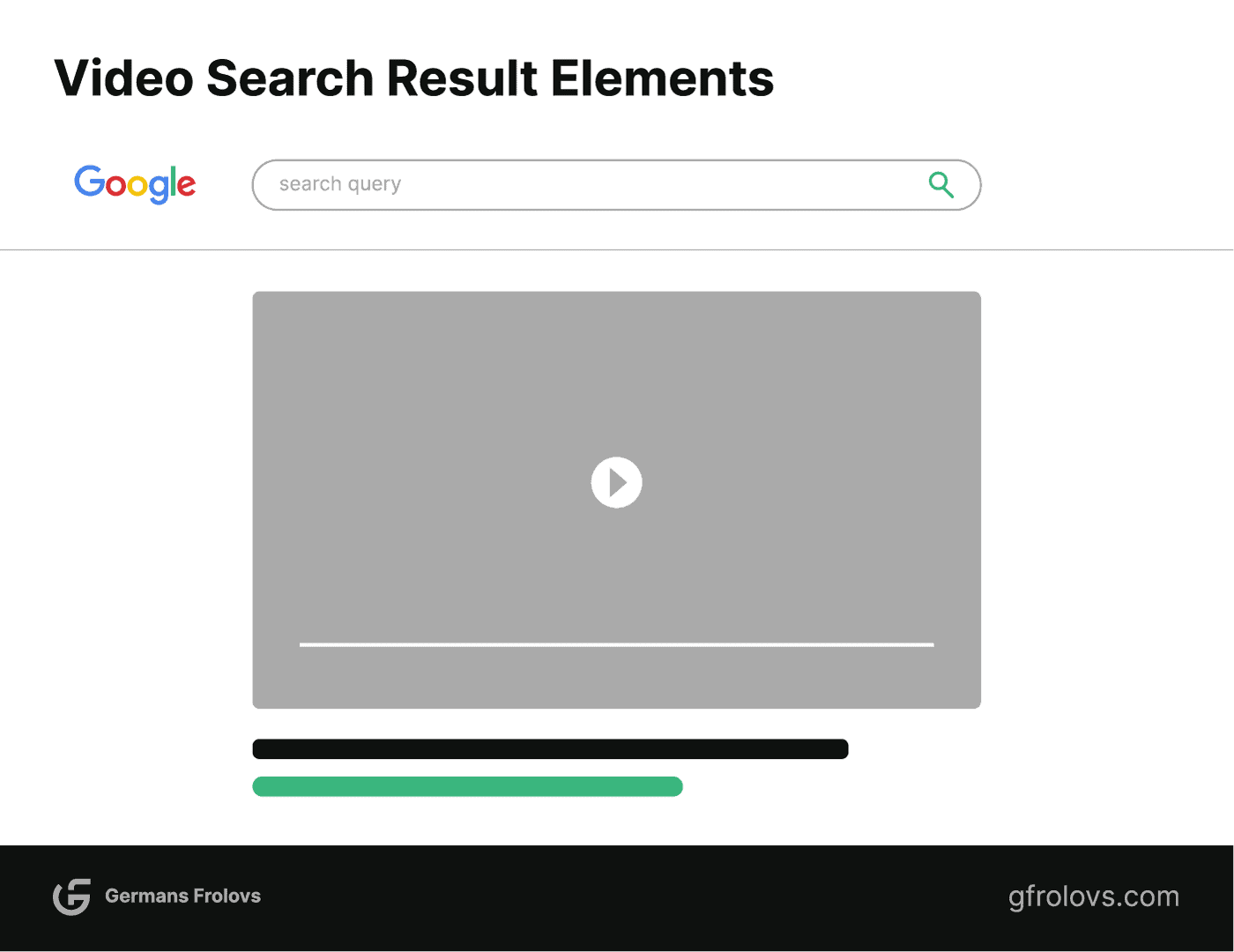
Video Searches
When users search for video content, like “how to bake a cake,” search engines often present video results from platforms like YouTube or Vimeo. These video results can appear in a video carousel, where multiple videos are showcased in a horizontal layout, or as standalone organic results.
Shopping Searches
In response to product-related queries like “buy running shoes,” search engines often include shopping carousels within the SERPs. These carousels showcase products along with accompanying images, prices, and merchant information.
News-Related Searches
Based on the recency and relevance of a query, the SERP may incorporate carousels that highlight the latest news articles, tweets, or other social media posts pertaining to the topic.
These carousels provide users with real-time updates and diverse perspectives from news sources and social media platforms directly within the search results.
How SEO Works?
The biggest search engines like Google use highly complex algorithms to determine the ranking of websites on the search engine results page.
These algorithms take into account hundreds of factors, including website speed, content quality, keywords used, and more. Most of these are unknown to the public.
Also, not a single person at Google knows the exact algorithms used to rank pages since machine learning is involved and algorithms are constantly changing.
However, being aware of the following basic SEO principles can help you better understand how SEO works and what you can do to improve your website’s visibility.
Understanding the Target Audience
The first and foremost principle of SEO is understanding the target audience and their search behavior.
This includes identifying and assessing their pain points, and preferences, and most importantly using words that people would use to look for what you offer, also referred to as keywords.
By doing keyword research you can find out what these words are.
Here is how to get started with the keyword research:
- Go to any of the SEO tools with keyword research capabilities
- Enter one or a few relevant words or phrases
- Start looking through the list of suggested keywords and identify any that are related to your business
- Create a list of keywords most relevant to what you offer
- Group them into related topics and subtopics
- Prioritize topics and subtopics based on their business potential, search volume, and the overall competition
Crafting Relevant, High-Quality Content
Content is king when it comes to SEO.
With an understanding of the target audience and the words they use to look for content, it is essential to create high-quality, engaging, and relevant content that answers their questions and addresses their needs.
Content should be well-structured, informative, and regularly updated to maintain its relevance.
High-quality content not only attracts the audience but also draws the attention of search engines like Google, which rewards informative, unique, and valuable content with higher rankings.
Here are steps main steps you should take when creating content.
1. Align Content With Search Intent
Analyze the SERPs and craft content that aligns with the user’s search intent.
In other words, make sure your content answers the searcher’s question and provides an answer to their problem by looking at the content featured on the SERPs.
If search engines like Google think that the top-ranking pages are relevant enough to answer the searchers’ queries, then this is what you should strive for when creating content.
With that in mind, analyze the content type, content format, and content angle used by other top-ranking pages.
- Content type: Is it a blog post, product page, product category page, infographic, video, or perhaps a combination of more than one type?
- Content format: Is it a list post, a how-to guide, an expanded definition post, or a landing page featuring a tool or quiz?
- Content angle: Is there a unique angle or perspective that addresses the topic at hand like how low cost or how easy or fast it is to do something?
For example, let’s say you are targeting the topic “best free Android apps”.
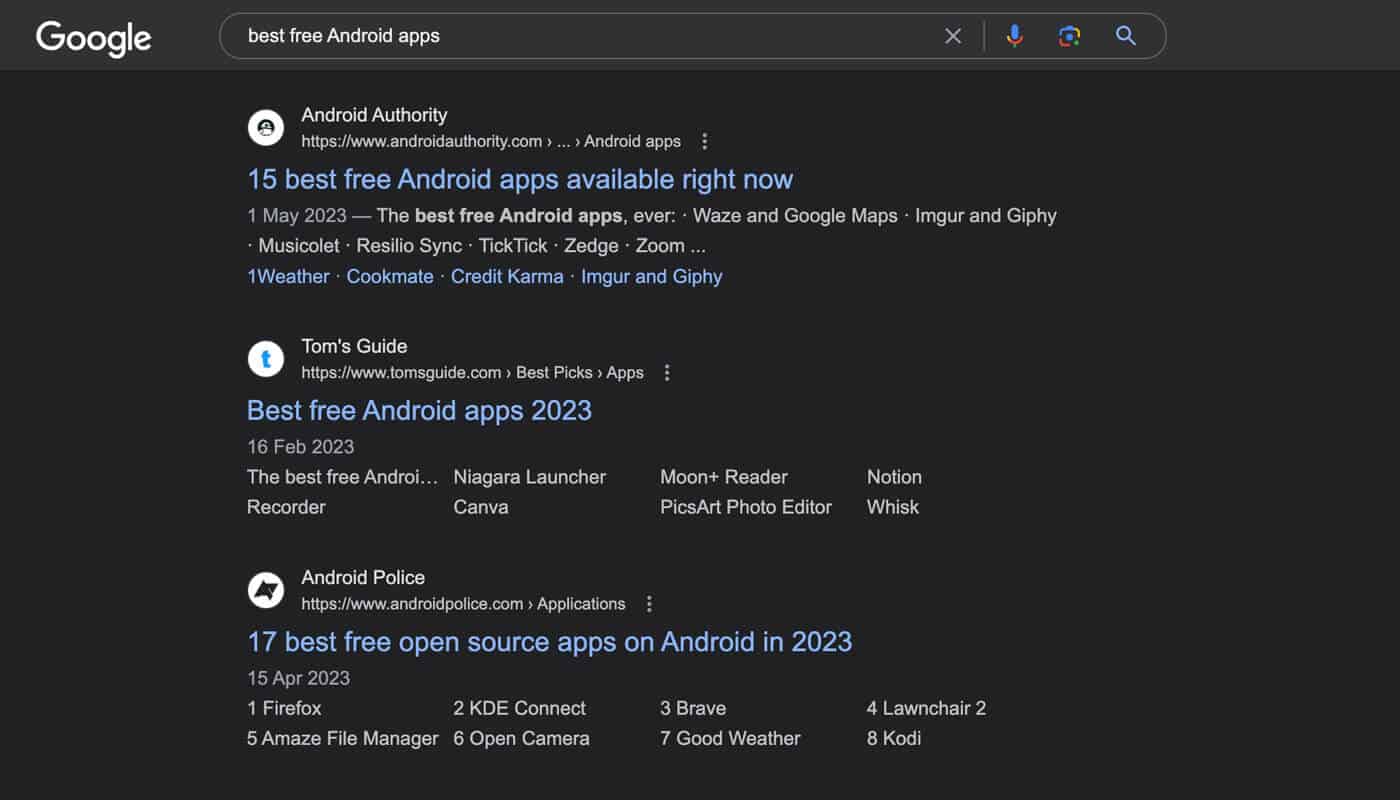
If we analyze the SERPs for the content type, format, and angle we see the following.
- Content type: It is a blog post.
- Content format: It is a list post.
- Content angle: The focus is on free apps and those relevant in 2023.
If we would want to rank for the topic “best free android apps”, we would have to create a blog post that provides a list of the best free Android apps you could download in 2023.
2. Cover the Topic Comprehensively
High-quality content should cover everything the searcher may want.
To create comprehensive content, consider the following practical methods.
- Research competitor content: Analyze top-ranking content on the same topic from various search engines – Google, Bing, YouTube, and others. Determine the range of subtopics covered, the depth of information provided, and any content gaps that could be filled to give your content a competitive edge.
- Utilize multiple sources: Don’t rely solely on Internet sources – check out books, research papers, case studies, and other expert materials.
- Explore niche forums and communities: Check online forums and communities related to your subject matter to gather insights, questions, and discussions relevant to your topic.
- Address related questions: Utilize Google’s “People Also Ask” feature and tools like AnswerThePublic, Reddit, and Quora to find common questions and topics related to your main topic.
3. Create Unique Content
It is important to create content that is unique and original.
Regurgitating existing information without providing any value may hinder your SEO efforts, as search engines reward originality and uniqueness.
Here are some practical ways to make your content stand out from the rest.
- Provide original research: Conducting your research projects and sharing the findings with your audience allows you to present new insights that are not readily available elsewhere. This could include surveys, experiments, or detailed data analysis specific to your industry or topic.
- Offer a unique perspective: Analyze the topic from a different angle or present a contrarian viewpoint that challenges conventional wisdom.
- Share personal experiences and case studies: Incorporate real-life examples, personal stories, or relevant case studies to make your content more relatable and engaging.
- Develop and share tools: Creating proprietary tools, applications, or resources that address specific problems or needs in your industry or niche can set your content apart from competitors. For instance, design custom calculators, templates, or checklists that offer practical assistance to your audience.
- Collaborate with industry experts: Invite guest contributors or industry influencers to share their expertise, perspectives, or insights on your website.
4. Optimize Content Design
Content design is the representation of information that aims to quickly and easily answer a user’s questions. It involves the arrangement of text, images, graphics, and other elements to create an aesthetically pleasing, easy-to-understand, and interactive experience for users.
Optimizing content design is essential for creating truly high-quality content.
Here are some practical ways to improve content design, ensuring that it effectively communicates with viewers in a digestible and engaging manner.
- Optimize text content for readability and skimmability: Use clear and concise language, and break up long blocks of text with headings, subheadings, bullets, and numbered lists.
- Include contextual images and graphics: Include images, graphics, and illustrations that are relevant to the content and help users understand complex concepts or processes.
- Utilize graphs and charts: When presenting data or statistics, use graphs and charts to visually represent the information, to make it easier for users to comprehend data at a glance.
- Embed videos or GIFs: Integrating relevant, high-quality videos or GIFs can engage users, increase time spent on a page, and improve overall content retention.
- Break up content with white space: Utilize white space effectively to give your content room to breathe and make it less overwhelming for the user. This includes using adequate margins, line spacing, and paragraph breaks to create a more comfortable reading experience.
- Prioritize mobile friendliness: Ensure that your content is designed to be easily consumed on mobile devices. Responsive mobile design, optimized images, and appropriately-sized text can significantly improve the user experience on smaller screens.
- Utilize interactive features: Adding interactive elements such as quizzes, polls, or multimedia content into your articles can engage users, increase dwell time, and help to communicate complex information in an entertaining and relatable way.
Optimizing Content for Discoverability
It’s essential to optimize your high-quality content for discoverability to ensure that it gets the attention it deserves.
Here are some basic strategies to optimize your content so search engines can discover it more easily.
1. Include Keywords in Prominent Locations
The most important locations where to include your keywords are listed below.
- Title: Incorporate the primary keyword in the title tag, as this helps search engines understand the topic of your content and signals relevant to the searcher’s intent.
- Headings: Include relevant keywords in headings and subheadings (H1, H2, H3, etc.). This helps search engines gauge the structure, hierarchy, and contextual flow of your content.
- Image file names: Try to include the target keywords in the file names of images, as this helps search engines understand what the image is about.
- Image alt text: Add your target keyword to the alt text of images. Search engines use this information to further understand the context and relevance of the image.
- Link texts: When linking to your page from another page on your website, make sure to use descriptive anchor text that contains the target keyword.
2. Increase Semantic Richness
Semantic richness refers to the use of diverse yet related terms, concepts, and phrases within your content.
By employing a higher level of semantic richness, you can help search engines better understand the depth and context of your content.
To achieve high semantic richness you can implement the following tactics.
- Use synonyms, related terms, and variations of your target keywords throughout the content.
- Include subtopics that are related to your primary keyword, and address user queries in a comprehensive manner.
3. Optimize Titles and Meta Descriptions
Create unique, engaging, and keyword-rich titles and meta descriptions for each page of your website.
Ensure that both the title and meta description is relevant to the content and encourages users to click through to your web page.
When creating titles and meta descriptions, consider the following general criteria.
- Relevance: Ensure your title and meta description accurately reflect your content’s primary focus, topic, or subtopics.
- Length: Keep titles between 50-60 characters and meta descriptions between 150-160 characters. Adhering to these length restrictions helps ensure that your titles and descriptions appear properly on the SERPs without being truncated or cut off.
- Keyword placement: Include your primary keyword and its variations in both the title and meta description, preferably towards the beginning.
- Clarity and conciseness: Write clear, concise, and descriptive titles and meta descriptions that help users quickly understand the content of your page. Avoid using jargon, excessive punctuation, or overly complex language.
- Compelling language: Consider using persuasive language and action verbs in your title and meta description to encourage clicks and engagement. Including phrases like “learn more,” “book appointment,” “discover,” or “find out” can motivate users to visit your page and explore your content.
- Differentiation: Craft unique titles and descriptions for each page on your website to avoid duplicate content issues and help search engines differentiate between individual pages.
For example, a non-optimized title and meta description for a local hairdresser website’s homepage might look like the following:
- Title: “Hair Services – Our Website”
- Meta description: “Visit our website to learn more about our hair services and book an appointment.”
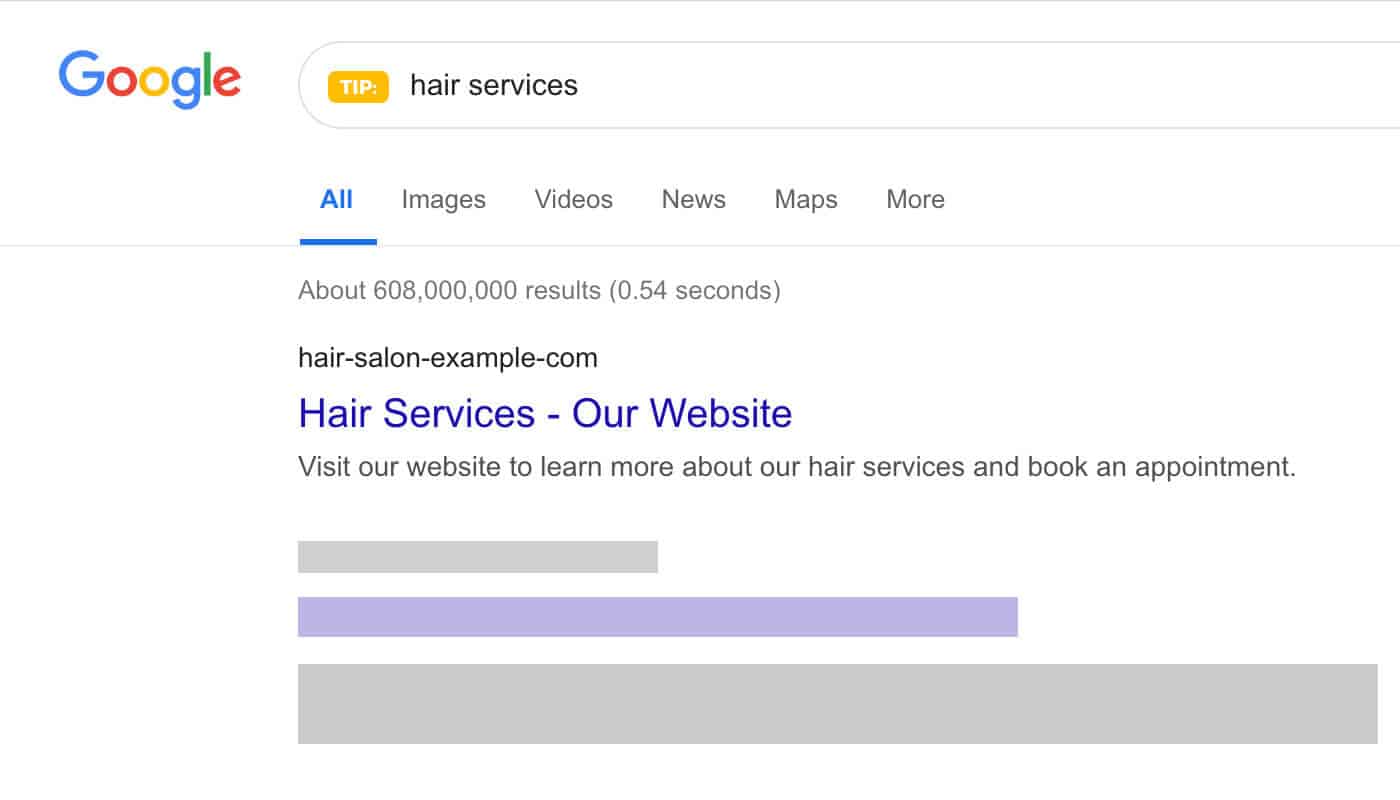
In this example, the title and meta description are both generic and lack specific information about the local hairdresser. The target keywords related to the business are not mentioned. Additionally, the meta description does not provide any unique or compelling reason for users to click.
On the other hand, below is an example of better-optimized metadata (title and meta description) for the same local hairdresser homepage.
- Title: “Flower Hair Salon: Expert Haircuts & Styling in [City Name]”
- Meta description: “Discover the finest hairdressing experience at Flower Hair Salon. Our talented stylists specialize in personalized haircuts. Book your appointment!”
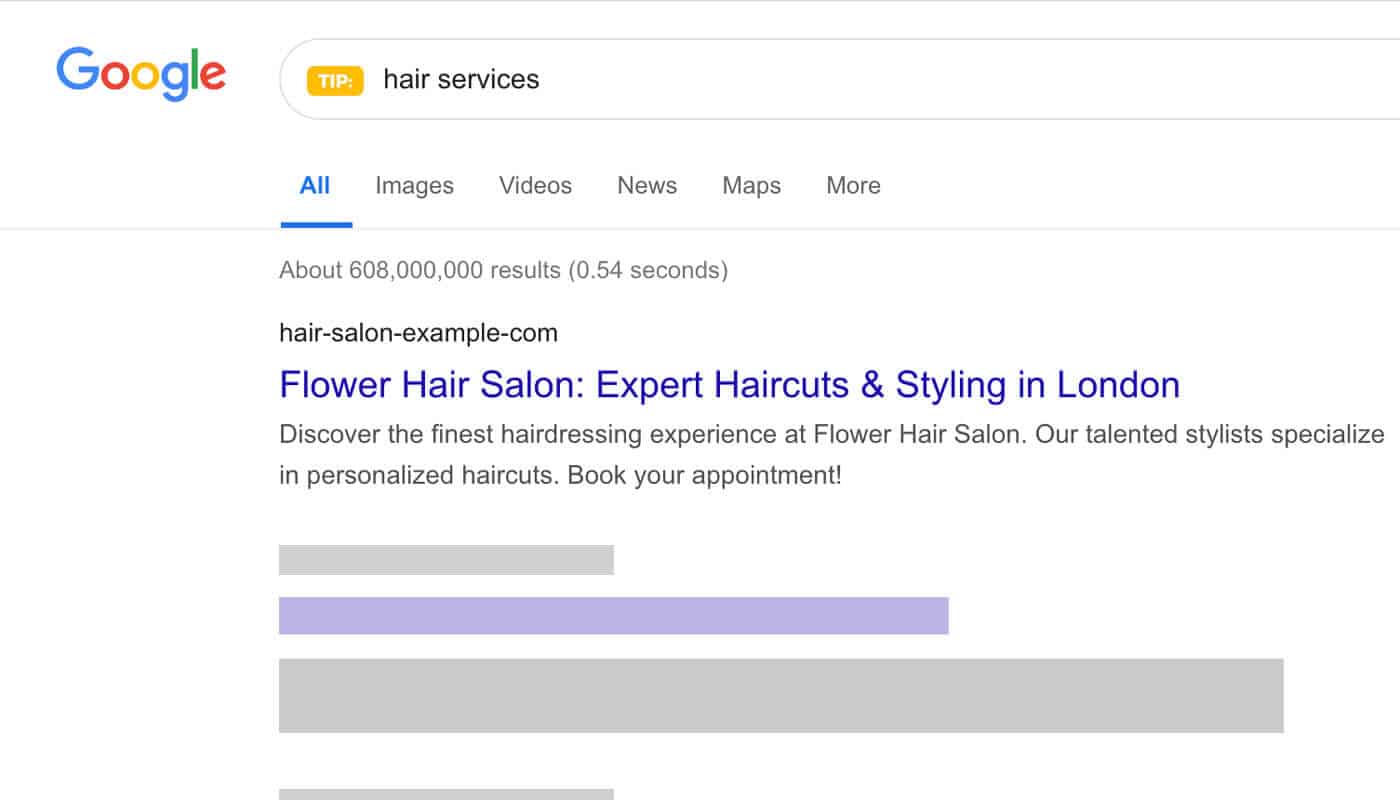
In the example above, the title and meta description includes the business name (Flower Hair Salon) and the relevant target keywords such as “haircuts”, “styling”, and the city name. The meta description provides useful information about the salon’s services and encourages users to book an appointment.
4. Create Internal Links
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page on your website to another page on your website. They work to establish a structure for your site, direct users to related content and resources, and help search engines better crawl, process, and understand the relationships between your pages.
Below are several best practices to follow when creating internal links.
- Naturally, connect your content by linking from one relevant page to another page within your site.
- Use meaningful, descriptive, and keyword-rich anchor text.
- Avoid using generic phrases like “click here” or “learn more.”
- Whenever you publish new content, review your existing content to identify opportunities for incorporating internal links to the newly published material. This approach ensures that your new content is effectively “plugged” into your site’s structure, making it more accessible to users and more easily discovered by search engines.
Providing Great Page Experience
Google rewards content that provides a good page experience.
However, the site owners should not focus on one of a few aspects but on an overall page experience across various aspects.
Some best practices to follow when working to provide a great page experience are listed below.
- Using HTTPS: Google has recognized the importance of a secure web, and since 2014, it has been using HTTPS as a ranking signal. To provide a secure browsing experience, obtain and install an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate for your website and migrate your site from HTTP to HTTPS.
- Making the website mobile-friendly: Having a mobile-friendly website means that it adapts seamlessly to different devices and provides an optimal user experience. Google has also adopted a mobile-first indexing approach, prioritizing mobile-friendly sites in its search rankings.
- Ensuring pages load fast: Ensure that your website loads quickly, as both Google and users appreciate fast-loading pages. Consider using tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights to measure and optimize your site’s loading times.
- Avoiding too many ads and pop-ups: Google has also taken a stance against intrusive interstitials (pop-ups) that hinder accessibility. Opt for user-friendly ad placements and minimal pop-ups to maintain a smooth and enjoyable browsing experience for your users.
- Improving Core Web Vitals (CWV): Core Web Vitals is a set of performance metrics introduced by Google that measure the user experience on a website. Although improving your website’s Core Web Vitals will lead to a better user experience, it is not something that will hinder your SEO performance dramatically.
Building Authority by Acquiring High-Quality Links
Google uses links to determine the relevancy of web pages and considers the quality and quantity of backlinks as a significant ranking factor.
However, it is important to note that links that intend to manipulate rankings, also known as link spam, are against Google’s guidelines. This includes practices like buying links or using manipulative tactics to generate artificial links, which may result in penalties or even removal from the search index.
To build website authority ethically and sustainably, you should focus on acquiring high-quality links through specific link-building strategies also referred to as off-page SEO.
Some popular and effective methods include guest blogging, creating linkable assets, and partnering with influencers or industry organizations.
Guest blogging, or guest posting, involves contributing articles or other content to authoritative, relevant, and reputable websites within your industry or niche. By providing valuable content to these sites, you can gain exposure to a wider audience, demonstrate your expertise, and acquire backlinks from authoritative sources.
Linkable assets are high-quality, informative, and engaging pieces of content on your website that naturally attract backlinks from other websites. Popular examples of linkable assets include Ultimate Guides (just like this one 😊), resource pages, in-depth case studies, data-driven research, infographics, and interactive tools or applications.
Collaborating with industry influencers, and organizations can also be a powerful way to gain exposure and acquire authoritative backlinks.
For instance, you can:
- Contribute to an article or round-up post and share your expertise and get a link to your site.
- Co-host webinars or events with industry leaders and include a backlink to your site in promotional materials.
- Offer testimonials or case studies to trusted partners or service providers, which may feature a link back to your website.
Measuring Results and Continuously Optimizing
To ensure the ongoing success of your SEO efforts, it’s important to measure the results and continuously optimize your website.
This process allows you to identify what works well, pinpoint areas that need improvement, and make data-driven decisions to achieve your goals.
Some best practices for measuring results and optimizing your SEO efforts are listed below.
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Determine which metrics are most important for your business, such as organic traffic, sales, form submission, free trials, or others.
- Regularly monitor metrics and analyze performance: Use tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and various third-party SEO tools to monitor and analyze your website’s performance. Regularly review the data to identify trends, patterns, and areas of improvement.
- Conduct SEO audits: Periodically conduct comprehensive SEO audits to evaluate your website’s overall performance, including on-page SEO optimization, technical errors, backlink profile, and content quality. Identify areas that need improvement and develop a plan to address them.
- Stay informed and adapt to changes: The world of SEO is dynamic. Search engine algorithms constantly evolve, the weight of SEO ranking factors change, and user behavior and industry trends shift over time. Be proactive in staying informed about the latest developments and adapt your strategies to maintain a competitive edge.
By following these SEO basic principles and focusing on measuring results and continuous optimization, you create a virtuous cycle that leads to improved performance, and increased organic traffic. This flywheel effect ensures that your SEO efforts become self-sustaining, continuously building upon previous successes and propelling your business to new heights.
What Are SEO Ranking Factors?
SEO ranking factors are the specific criteria that search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo! use to evaluate, rank, and display websites and their content in search engine results pages.
There are hundreds of ranking factors, and their importance may vary depending on the type of query, user behavior, location, device, and other variables.
SEO specialists continuously strive to understand and optimize for these factors in order to improve the visibility of their websites and attract more organic traffic.
While the precise number and specifications of ranking factors are not publicly disclosed and can undergo frequent changes due to algorithm updates, certain foundational factors have remained consistently important over time.
In no particular order, the top SEO ranking factors are:
- Quality content
- On-page optimization
- Internal links
- External links
- Mobile-friendliness
- Page speed
- Page experience
- HTTPS
1. Quality Content
Content is considered one of the most important SEO ranking factors.
High-quality, relevant, engaging, and SEO-optimized content that addresses users’ needs and problems is more likely to be rewarded with better rankings and visibility in SERPs.
2. On-Page Optimization
Proper on-page optimization, including the strategic use of title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, image tags, and structured data markup, can greatly influence a page’s ranking potential.
These elements help search engines understand the content and context of a page, allowing them to better assess its relevance and quality.
3. Internal Links
An effective internal linking strategy can improve search engine crawlers’ understanding of your site’s structure and establish relationships between pages.
This can lead to improved crawling, increased relevance, and better ranking performance.
4. External Links (Backlinks)
External links or backlinks are considered one of the most influential ranking factors due to their role as “votes of confidence” or endorsements from other websites.
Search engines use links as a signal in determining the relevance of web pages as well as view these links as indicators of a page’s authority, quality, and usefulness.
More high-quality and relevant backlinks typically translate to better rankings, according to Google’s Andrey Lipattsev, in 2016, high-quality backlinks are one of Google’s strongest ranking factors.
5. Mobile-Friendly Site
Mobile-friendliness or responsive design has become an increasingly important factor in recent years due to the growing number of users accessing the internet via smartphones and tablets.
A mobile-friendly site adapts to various screen sizes and devices, providing an optimal user experience.
6. Page Speed
Search engines consider page speed when evaluating web pages.
Faster page load times not only lead to a better user experience but can also contribute to higher search engine rankings.
7. Page Experience
Search engines like Google prioritize pages that offer a great user experience and rewards sites that provide that.
Aspects like security, Core Web Vitals results, intrusive interstitials, the number of ads that interfere with the main content, navigation, and previously mentioned page speed can all affect the overall page experience.
8. HTTPS
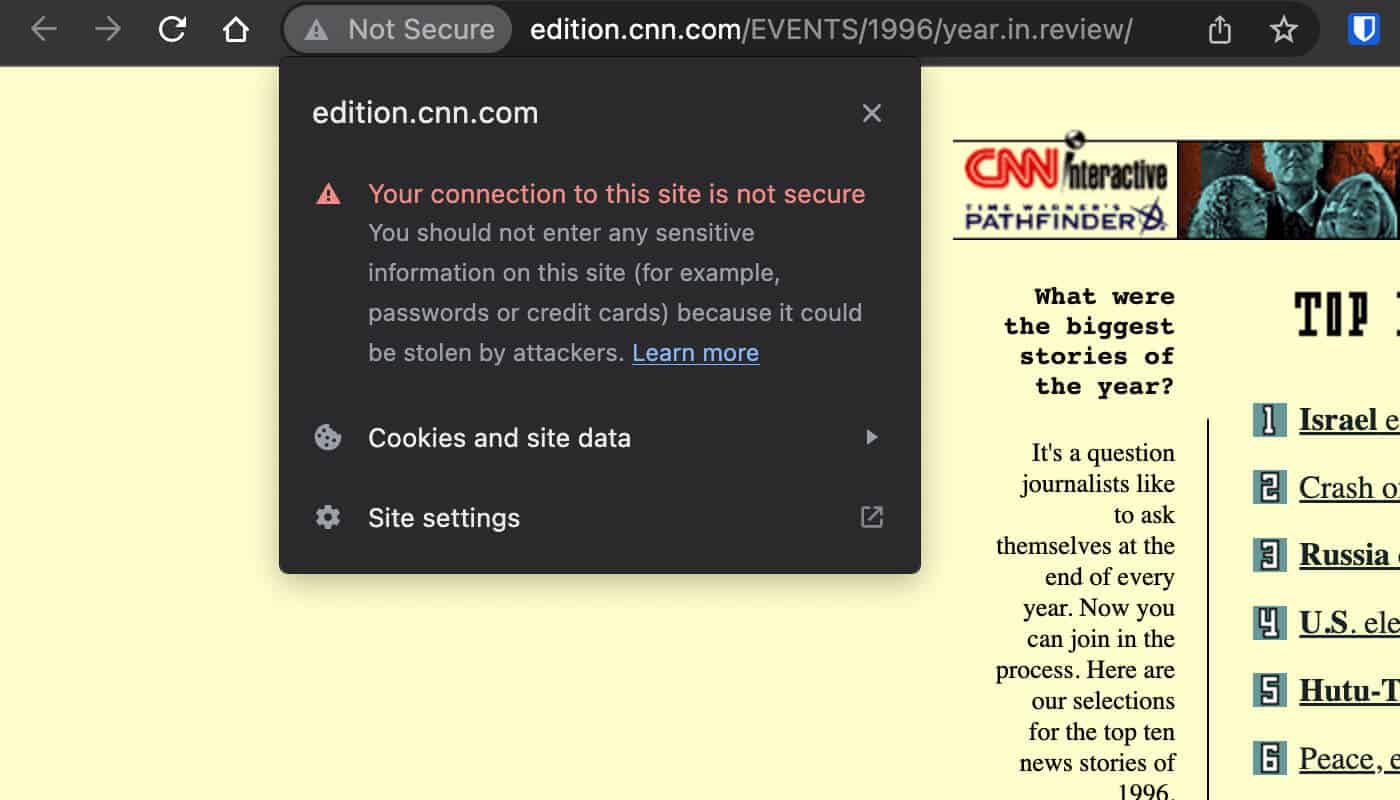
The use of HTTPS has become a lightweight ranking factor since 2014, as search engines like Google consider the security of a website important in providing a safe browsing experience for users.
If you notice a “Not Secure” warning in your browser, it means that the website does not use HTTPS. In this case, a TLS certificate should be installed.
What Are the Types of SEO?
There are three main types of SEO – on-page, off-page, and technical SEO.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to the practice of optimizing the content on a web page.
The goal of on-page SEO optimization is to help search engines understand what the web page is about so they can match it to relevant search queries better.
What Does On-Page SEO Include?
Some main components of on-page SEO include the following.
- Keyword research: A crucial step in optimizing your on-page SEO is conducting keyword research. It involves identifying and targeting relevant keywords that align with your business or service and cater to the needs of your target audience.
- Content optimization: Creating high-quality, engaging, and relevant content that addresses user needs and problems, while also incorporating your target keywords in a natural and meaningful way.
- Title tags: Crafting unique, informative, and keyword-rich title tags that accurately represent your content and signal its relevance to search engines.
- Meta descriptions: Writing descriptive meta descriptions that include your target keywords and encourage users to click on the results.
- Heading tags: Implementing proper heading tag hierarchy (H1, H2, H3, etc.) with target keywords to help search engines understand the hierarchy and context of your content.
- Image optimization: Ensuring all images have descriptive file names and alt text that include your target keywords.
- Internal linking: Strategically placing internal links within your content to guide users and search engine crawlers to other relevant pages on your website.
- User experience: Optimizing elements such as page layout, readability, and multimedia integration to ensure a positive browsing experience for your visitors.
What is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO is all about the optimization activities that take place outside of your website. It is primarily associated with link-building – getting other websites to link to your website and the page you are trying to optimize.
Links have been baked into Google’s algorithm since day one, as they aim to help search engines like Google understand how relevant your web page is to users.
To this day, improving your website’s rankings on Google heavily relies on off-page SEO optimization and the acquisition of high-quality backlinks, especially for higher competition queries.
What Does Off-Page SEO Include?
Some of the primary off-page SEO methods are listed below.
- Brand marketing: Creating a strong brand identity and increasing brand awareness through various channels ensures that users can easily recognize and associate your brand with a specific niche or industry.
- Public Relations (PR): PR involves managing your brand’s reputation by distributing press releases, collaborating with influencers, or getting media coverage to generate a buzz about your brand.
- Content marketing: Creating and sharing valuable content that answers user questions, provides insights, solves problems, and establishes your brand as an authoritative and trustworthy source.
- Social media marketing: Utilizing social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, Pinterest, and others to promote your brand, and content, and connect with your audience.
- Listing management: Ensuring that your business is listed on relevant and authoritative online directories, local listings, citation listings, and niche-specific websites. Accurate and consistent listing information contributes to local SEO success.
- Ratings and review management: Encouraging customers to leave reviews and ratings on various platforms like Google Business Profile, Yelp, G2, Capterra, TrustRadius, Trustpilot, and others (depending on the type of business), as well as actively responding to all of them.
- Forum participation: Engaging with online communities, forums, and discussion platforms relevant to your industry.
- Other link building: Acquiring high-quality backlinks from authoritative and relevant websites via various other strategies such as guest posting, influencer outreach, and many others.
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing a website’s technical aspects to ensure that search engines can crawl, index, and render the site efficiently.
It serves as an indispensable foundation for any website since without proper implementation of technical SEO, even the most exceptional website content would remain hidden from search engines.
What Does Technical SEO Include?
The core components of technical SEO are listed below.
- Site architecture: An organized site architecture with clear navigation, and proper internal linking.
- Page speed: Page loading speed, both on desktop and especially mobile, impacts both user experience and search rankings.
- Mobile-friendliness: Ensuring that your website is properly optimized for mobile devices is essential for providing a great user experience, especially with Google’s mobile-first indexing.
- XML sitemap: An XML sitemap lists all the important URLs on your website, helping search engines discover and index your content more efficiently. Regularly updating and submitting your sitemap to major search engines is an important part of technical SEO.
- Robots.txt: This text file provides instructions to search engine crawlers on which parts of your site they should crawl and which parts they should not crawl.
- Structured data: Adding structured data (Schema.org markup) helps search engines better understand your content and improves the way your site appears in search results through rich snippets and other search features.
- Clean and efficient code: Writing clean, valid, and efficient HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code helps search engines process your site more effectively.
- Website security: Ensuring your website is secure by implementing HTTPS (SSL certificate) provides a more secure browsing experience for users.
- Canonicalization: Implementing canonical tags helps prevent duplicate content issues by signaling to search engines which version of a page should be considered the primary version.
- 404 errors and redirects: Regularly monitoring and fixing broken links, and 404 errors, and implementing proper redirects (301 and 302) helps prevent users from encountering “dead ends”.
- Server performance: Optimizing server response times is important for site performance and user experience. Choosing a reliable and scalable hosting provider and monitoring server performance can help ensure your site loads quickly for all users.
What Are the Different SEO Specialities?
SEO is a broad field with various specialties that cater to different types of websites, businesses, and target audiences.
These specialties focus on specific aspects of SEO, incorporating unique techniques and strategies to improve the online presence and search rankings of a particular niche or industry.
Some of the major SEO specialties are explained below.
- E-commerce SEO: Focuses on optimizing online stores and e-commerce websites. eCommerce SEO involves optimizing product listings, category pages, on-site search functionality, and user experience.
- International SEO: Deals with optimizing websites for multiple countries or languages, targeting a global audience. It involves implementing geo-targeting techniques, hreflang tags, creating localized content, and ensuring a culturally sensitive user experience for various regions and languages.
- Enterprise SEO: Tailored for large, complex organizations with extensive websites that contain a massive number of pages and involve numerous stakeholders. This specialty concentrates on streamlining the on-page and off-page optimization, leveraging big data insights, and managing complex site structures while aligning with the organization’s business goals.
- Local SEO: Focuses on optimizing websites to rank higher in local search results. It targets a specific geographic area or audience and involves optimizing elements such as Google Business Profile listing, local citations, and location-based keywords to attract more nearby customers.
- SaaS SEO: SaaS (Software as a Service) SEO specializes in optimizing SaaS-based websites and applications to increase their online visibility, generate more leads, and drive customer acquisition. Key strategies include content marketing, keyword research tailored to SaaS offerings, and optimizing the user experience for better conversions.
- News SEO: Aims to optimize news websites, articles, and digital journalism content for better visibility in search engine news results and Google News. This specialty focuses on implementing structured data, optimizing headlines, ensuring timely and fresh content, and adhering to the Google News Publisher Guidelines to gain higher rankings in news search results.
- Programmatic SEO: A specialized approach that involves using scalable, data-driven, and automated techniques to optimize large websites with thousands or even millions of pages. This specialty focuses on leveraging programming languages, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), data analysis, and automation tools to streamline the SEO process and improve search rankings for a vast number of pages in an efficient manner.
- Mobile SEO: Specializes in optimizing websites and content explicitly for mobile devices. With the growing emphasis on mobile-first indexing, mobile SEO works on improving mobile-friendliness, site speed, and user experience on smartphones and tablets.
- Video SEO: Focuses on optimizing video content for better visibility and rankings in video search results on platforms such as YouTube and Google. It includes strategies like keyword research for video, optimizing video titles, descriptions, and tags, and enhancing user engagement.
- Image SEO: A specialized branch that focuses on optimizing images on a website to improve its visibility within search engine image results like Google Images, as well as general search results. This specialty involves using techniques such as proper image file naming, filling out alt text attributes, image compression, responsive image display, and incorporating relevant keywords in the context surrounding the image.
These SEO specialties cater to the unique needs of businesses, industries, and target audiences, enabling tailored SEO strategies that result in higher search rankings, increased online visibility, and better overall performance.
What is SEO Strategy?
An SEO strategy is a comprehensive plan that encompasses various methods, techniques, and goals aimed at optimizing a website to achieve higher rankings on SERPs.
It involves a combination of on-page, off-page, and technical SEO practices, along with the basic SEO principles.
The primary objective of an SEO strategy is to maximize website visibility, drive traffic, and increase conversions and achieve business objectives.
What are the SEO Tools That Could Help?
There are various SEO tools available that can help with different aspects of your SEO optimization efforts, ranging from free to paid options.
The main SEO tools that could help you implement an optimal SEO strategy are the following.
- Google Search Console (GSC): This is the most essential tool for content and technical SEO analysis. It allows you to monitor website performance, identify technical issues, and gain insights on search rankings and visibility.
- Google Analytics (GA): Google Analytics allows you to track and analyze website traffic, user behavior, and conversions to measure the effectiveness of your SEO strategy. In fact, it is a universal website traffic analysis tool that can also be used by other marketing professionals for analysis of Search Engine Marketing (SEM) and Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaigns.
- Keyword research tools: Using a tool for keyword research you will be able to identify relevant keywords and phrases to target in website optimization efforts. By utilizing free keyword research tools such as Google Keyword Planner, and Keyword Surfer, or free versions of premium tools like SEMrush, or Ahrefs, you can discover high-volume and low-competition keywords, understand search trends, and identify keyword variations for creating and optimizing content.
- All-in-one SEO software suite: SEO tool suites offer a comprehensive set of tools and features to streamline and optimize various aspects of your website. Tools like Moz, SEMrush, or Ahrefs, provide insights into keyword research, competitor analysis, backlink monitoring, site audits, and more. They enable you to track keyword rankings, analyze website performance, identify technical issues, and discover opportunities for improvement. Most of these tools are premium but some also offer pretty generous free versions such as Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
- Other specialized SEO tools: There are several specialized SEO tools that provide targeted functionality and insights to optimize specific areas of your website. Ranging from SEO plugins for WordPress sites like Yoast SEO and RankMath to website crawling tools such as Screaming Frog and Sitebulb, to content optimization solutions like Surfer, Marketmuse, and Clearscope to many other tools.
My recommendation is to select tools that align with your specific needs and leverage the suite’s features to optimize your website effectively.
Implementing an effective SEO strategy is possible using only free tools such as Google Search Console (GSC), free keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner or Keyword Surfer, and Ahrefs Webmaster Tools.
The first tool I would suggest spending money on while considering the budget would be one of the cheaper SEO tool suites such as Ubersuggest or Mangools.
That being said, you might be wondering what is my personal SEO tool stack.
SEO tools that I currently use the most are the following.
- Google Search Console (GSC) for organic visibility analysis and technical issues.
- Pirsch Analytics for privacy-friendly website traffic analysis.
- Ahrefs Webmaster Tools streamline the overall website’s SEO performance.
- SEOcrawl for SEO reporting, dashboards, and more.
- NEURONwriter for content optimization.
- Larseo for the keyword, traffic, and backlink research.
- SERPROBOT for keyword rank tracking.
- WebSite Auditor for website crawling.
What Courses for Learning SEO Are There?
The following list includes some of the courses for learning SEO, divided into paid and free options.
These courses cover everything from search engine algorithms to keyword research and on-page SEO to technical SEO optimization, and link-building strategies.
Paid SEO courses:
- Bruce Clay SEO Training & Membership Program (Bruce Clay)
- SEO Course (ClickMinded)
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Training Course (Simplilearn)
- SEO Essentials Certification (Moz)
- The (Non-Techie) Marketer’s Guide to SEO (MarketingProfs)
Free SEO courses:
- SEO Certification Course (Hubspot)
- SEO Training Course (Ahrefs)
- Blogging Course for Businesses (Ahrefs)
- SEO Training for Beginners (Yoast)
- SEO Training for Beginners (Shopify)
- SEO Crash Course with Brian Dean (Semrush)
- On-Page and Technical SEO Course (Semrush)
- SEO Fundamentals Course with Greg Gifford (Semrush)
- Advanced Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Program (Simplilearn)
How is SEO Different From SEM and PPC?
You might be wondering, what’s the difference between SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and SEM (Search Engine Marketing), or even SEO and PPC (Pay-Per-Click)?
Read on to learn more about both SEM and PPC and how they’re related to SEO.
What is the Difference Between SEO and SEM?
The main difference between SEO and SEM lies in their strategies and goals.
SEO focuses on improving a website’s visibility, ranking, and organic traffic (non-paid).
On the other hand, SEM involves both organic and paid advertising strategies to increase website visibility on search engines. It includes SEO best practices and adds paid advertising techniques like PPC, and remarketing, using platforms such as Google Ads and Bing Ads.
In other words, SEO can be considered one-half of SEM, as it is a crucial component of the larger umbrella of search engine marketing. While SEM includes both organic and paid strategies to enhance website visibility and drive traffic, SEO specifically focuses on optimizing a website to improve its organic search rankings.
Therefore, SEO is a vital and integral part of SEM, working together with paid advertising techniques to form a comprehensive online marketing strategy.
What is the Difference Between SEO and PPC?
The main difference between SEO and PPC lies in their approach to generating website traffic, with SEO focusing on non-paid organic rankings and PPC involving paid advertisements with a cost per click.
SEO focuses on optimizing the website with the aim of increasing its visibility and ranking on organic or non-paid parts of the search engine results page.
PPC, on the other hand, is a paid advertising model where businesses bid on specific keywords to display their ads on search engines. Advertisers pay a fee each time their ad is clicked by users.
PPC can provide immediate visibility and drive targeted traffic to a website. While SEO is a long-term strategy that aims to establish a strong organic presence, resulting in sustainable traffic and reducing the reliance on paid advertising.