SEO Content: The Beginner’s Guide to Content Creation
Updated:
SEO content is digital content specifically crafted to rank highly in search engine results pages (SERPs), driving organic traffic to a website and increasing its visibility.
To create high-quality SEO content, selecting a relevant topic, analyzing search intent, covering the topic comprehensively, and optimizing the content for discoverability are integral steps.
An effective SEO content strategy encompasses setting clear goals, analyzing the target audience, planning content production, optimizing distribution channels, and regularly reassessing the overall approach.
Various types of SEO content, such as blog posts, product pages, and videos, can cater to different search intents. Content also needs to be visually appealing, easily digestible, and provide a good overall user experience.
Monitoring and analyzing the performance of the content strategy help identify areas of improvement, make data-driven decisions, and optimize the content’s impact.
By following these guidelines, effective SEO content can be crafted to attract organic traffic, resonate with the target audience, and improve search engine rankings.
Table of Contents
What is SEO Content?
SEO content is a type of digital content that is specifically created to rank highly in search engine results pages (SERPs). The primary goal of SEO content is to drive organic traffic to a website, ultimately increasing its visibility and attracting potential customers or readers.
Why is SEO Content Important?
Creating high-quality, SEO-optimized content is essential for gaining visibility in search engine results, attracting organic traffic, and harnessing the power of Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
Not all content ranks well and gets traffic from search engines. In most cases, only content specifically created for people searching about the topic ranks well – that is the main reason why SEO content is important.
What Are the Types of SEO Content?
Here are various types of SEO content:
- Blog posts: These are articles typically published on a website’s blog section, covering various topics related to the industry or niche.
- Product pages: Product pages showcase specific products or services, providing detailed descriptions, features, and benefits to persuade potential customers to make a purchase.
- Product category pages: These pages group similar products or services together, making it easier for visitors to navigate and find relevant offerings.
- Landing pages: Designed for marketing campaigns or lead generation, landing pages provide targeted information and a clear call to action, driving users toward a specific goal.
- Guides: Guides offer in-depth, comprehensive information on a particular subject.
- Listicles: A combination of “list” and “article,” listicles are easy-to-read, engaging pieces that present information in a numbered or bulleted format.
- Videos: Engaging and visually appealing, videos can be used to explain complex concepts, share stories, or demonstrate products and services.
- Glossaries: Provide definitions and explanations of industry-specific terms, helping users better understand the subject matter.
- Directories: Collections of links and resources, usually organized by topic or industry.
- Case studies: By showcasing real-life examples of a product or service’s success, case studies build credibility and help potential customers make informed decisions.
- Reviews: Offer readers valuable insights into a product or service’s quality and performance.
- Interviews: Interviews with industry experts or influencers can provide valuable insights and boost a website’s credibility.
- FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) provide answers to common user queries in a concise, easily digestible format.
- News and press releases: These timely articles share company updates or industry news.
- Infographics: Infographics present complex information or data in a visually appealing, easy-to-understand format.
- Interactive tools: Interactive tools, such as quizzes, calculators, or configurations, engage users and encourage them to spend more time on a website.
- Podcasts: Audio content, such as podcasts, can be used to share information, stories, or interviews.
These are some of the most common ones I could think of but I’m sure there are many more. Literally, any type of content can be optimized for search engines, as long as it is relevant and provides value to the audience.
How to Write SEO Content?
Creating high-quality SEO content involves several steps, from choosing a topic to optimizing the content for discoverability.
Let’s go through the process in more detail.
1. Choose a Topic
You should already have a topic in mind if you have done some keyword research.
The topic should align with your website’s niche and target audience interests, it should also have business potential and search demand.
Let’s assume that you have chosen “breakfast recipes” as your topic.
2. Find a Primary Keyword
The next step is to identify a primary keyword that accurately describes the main theme of your content. You should also ensure that it aligns with the criteria mentioned above, and is not too competitive.
To find the primary keyword for your topic, employ tools such as using Google’s Autocomplete, Google’s Related Searches, Google Keyword Planner, Google Trends, or any of the keyword research tools like Ahrefs or Semrush.
For example, using Google’s Autocomplete you can find long tail keywords that people are already searching for, such as “healthy breakfast recipes”.
TIP
To assess the competition of the SERP, you can use any of the free Chrome Extensions such as MozBar or Keywords Everywhere that show a Domain Authority (DA) rating of the ranking website. SERPs with low DA websites are usually less competitive.
Let’s continue with the primary keyword “healthy breakfast recipes”.
3. Analyze Search Intent
Understanding the search intent behind your primary keyword means knowing what users hope to find when searching for that search query (your primary keyword).
With some experience, you will be able to identify the search intent just by looking at the SERP.
There are four general types of search intent: informational, navigational, transactional, and commercial investigation. Here is a brief overview of each one:
- Informational: Users are looking for information about a specific topic. For example, if the user is searching “healthy breakfast recipes”, they may be looking for information on healthier food options to start their day.
- Navigational: Users are looking for a certain website or web page. For instance, if the user is searching for “Mcdonald’s menu”, they might be trying to find Mcdonald’s main website or its official menu page.
- Transactional: Users have decided what they want and are just looking for a way to purchase it. For example, “buy healthy breakfast recipes book”.
- Commercial investigation: Users are researching a product or service before making a purchase. They might be looking for product comparisons, reviews, customer experiences, etc. For example, the user may search “best healthy eating books” to get an overview of what’s available in the market.
However, for some keywords, it can be more challenging to identify the search intent.
In these cases, you will need to go a step further, and analyze the top-ranking pages on the SERP for:
- Content type: Is it a blog post, product page, product category page, infographic, video, or perhaps a combination of more than one type?
- Content format: Is it a list post, a how-to guide, an expanded definition post, or a landing page featuring a tool or quiz?
- Content angle: Is there a unique angle or perspective that addresses the topic at hand like how low cost or how easy or fast it is to do something?
For example, the top results when searching for “healthy breakfast recipes” are all blog posts in a list post format. “Healthy” is the most dominant angle.
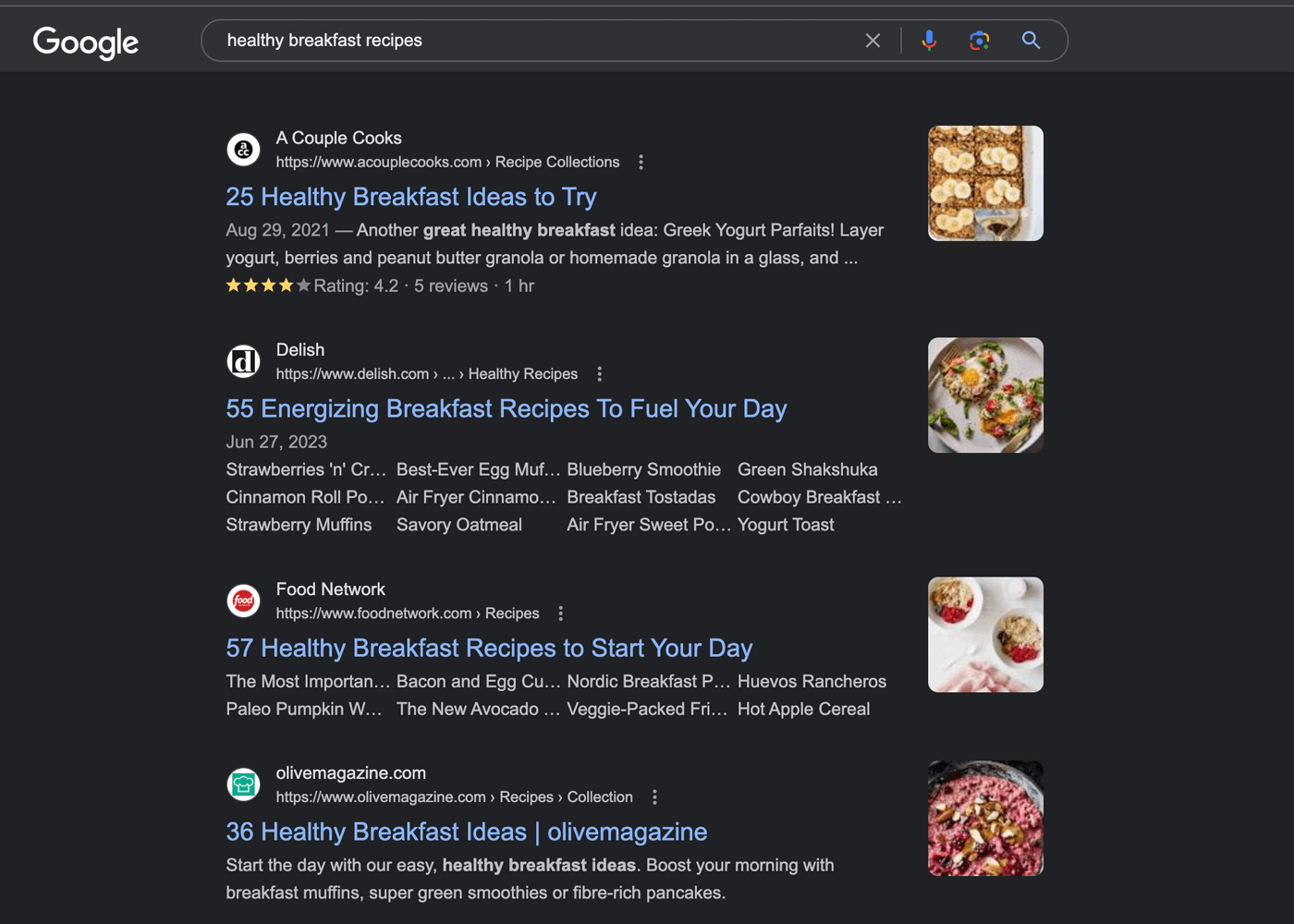
4. Cover the Topic Comprehensively
To create high-quality SEO content, you need to cover your chosen topic in full.
This means providing in-depth information, presenting new perspectives or insights, and offering solutions to all common problems or challenges.
To create comprehensive content, consider the following methods:
- Research competitor content across search engines, assessing the covered subtopics, looking for commonalities as well as identifying content gaps.
- If you do have access to a keyword research tool, analyze the top-ranking pages and their top-ranking keywords. In many cases, these keywords reveal the subtopics discussed in the content.
- Utilize diverse sources such as books, papers, case studies, and expert materials to gain new insights, and showcase thorough research.
- Explore niche forums and communities to gather real-world insights, questions, and discussions.
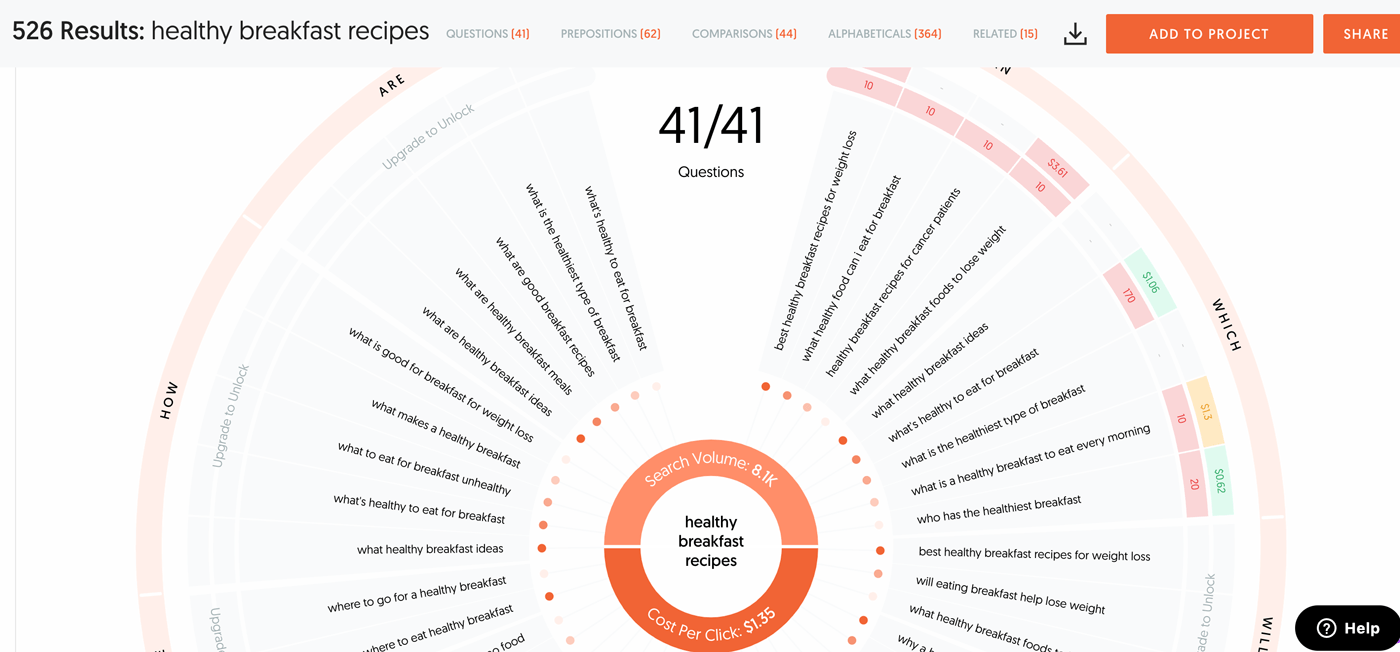
- Find related questions using the “People Also Ask” and tools like AnswerThePublic and QuestionDB to provide in-depth answers that increase the value of your content.
For example using AnswerThePublic and the keyword “healthy breakfast recipes” you can find potential search queries to answer such as:
- what are healthy breakfast ideas
- best healthy breakfast recipes for weight loss
- what is the healthiest type of breakfast
- healthy breakfast recipes for cancer patients
5. Make the Content Unique
Search engines value originality, so make sure your content stands out from the rest.
To create unique content, you can:
- Conduct original research, such as surveys or data analysis, within your industry or topic to offer new insights.
- Take a different perspective or present a contrarian viewpoint.
- Incorporate personal experiences, real-life examples, and relevant case studies.
- Create tools, applications, or resources that address specific problems.
- Collaborate with industry experts, guest contributors, or influencers to share their expertise and insights.
6. Optimize Content Design
Your content should not only be informative but also visually appealing, easy to read, and provide a good overall user experience. This involves optimizing the design of your content, such as its layout, length, images, and multimedia.
To optimize your content design, consider the following best practices:
- Break up large blocks of text with headings, subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists.
- Use whitespace to provide visual breaks and help guide the reader’s eye through your content.
- Use high-quality and relevant images, infographics, and videos to illustrate key points and keep users engaged.
- Include graphs and charts to visually represent data and statistics, making complex information easier to understand.
- Ensure that your content is mobile-friendly, responsive, and accessible to all users.
For our example, healthy breakfast recipe example, I would consider adding eye-catching images of each breakfast recipe. Along with step-by-step instructions and helpful charts detailing nutritional information.
7. Optimize Content for Discoverability
Now that your content piece looks great, you will need to make sure it’s easily discoverable by both search engines and readers alike.
To do this, make sure to implement some of the general on-page SEO best practices such as:
- Include your primary keyword(s) in prominent locations such as the title, headings, and meta description.
- Use related keywords throughout the content.
- Create a compelling meta title and description.
- Use header tags (H2, H3, H4, etc.) for section headings to create a logical contextual flow of information.
- Create user-friendly URLs with the primary keyword and short, descriptive terms.
- Write descriptive, keyword-optimized image alt tags.
- Add internal and external links to relevant resources.
These are just some of the basic on-page SEO elements you should include in your content, but there are many more you can consider for further on-page SEO optimization. However, optimizing your content for search engines involves more than just on-page elements. It requires a comprehensive SEO content strategy that encompasses various aspects of content creation and promotion.
How to Develop an SEO Content Strategy?
Developing an effective SEO content strategy involves setting clear goals, analyzing your target audience, planning content production, optimizing distribution channels, and regularly analyzing and reassessing your overall SEO strategy.
Here are the key steps described in more detail.
1. Define Your SEO Content Strategy Goals
Before starting, it’s essential to set clear and measurable goals for your content strategy.
These goals will help guide your content creation and optimization efforts.
First, determine your goals as a website or business, for example:
- Are you looking to drive sales through your website?
- Do you want to generate more leads?
- Do you monetize your website via ads and therefore just want to increase traffic and have readers return to the site?
If your primary goal is to drive sales, you will need to create product pages and ensure that they are optimized for SERP visibility. Then focus on creating informative articles that offer solutions to customer problems and link to the product pages.
If, on the other hand, your primary goal is lead generation, you will need to focus on creating product/solution pages and landing pages, as well as informative content that naturally leads to the product/solution page or a call-to-action to contact you.
If your websites operated on an ad monetization model, you can focus on creating content that attracts organic search traffic and encourages readers to visit multiple pages on your website.
Perhaps your goal is a combination of some of these?
For instance, a website about recipes could focus on driving sales by creating cookbooks, as well as monetizing through ads placed in blog posts generating organic traffic.
2. Analyze Your Target Audience
To create content that resonates with your audience, you need to understand who your target audience is and what their needs, preferences, and pain points are.
Analyze your target audience by:
- Creating buyer personas that represent your ideal customers or readers.
- Conducting surveys or interviews to gather insights about your audience’s preferences and challenges.
- Monitoring niche forums, communities, and social media platforms to understand their interests and discussions.
Then think about what kinds of content the target audience would be looking for.
For example, if you have a recipe blog targeting people looking for healthier options, content topics could include the health benefits of certain ingredients or recipes, meal-prepping tips, nutrition facts, etc.
3. Create an Editorial Calendar
An editorial calendar outlines the types of content you will create, the topics you will cover, and the publishing schedule.
Here are a few simple steps for creating an editorial calendar:
- Start with the topics that align with your content strategy goals.
- Create a list of primary keywords related to each topic, and identify potential subtopics.
- Determine the type of content you will create for each topic (blog post, product page, etc.).
- Map out the production process: research, writing, editing, optimization, design, distribution, and monitoring.
- Set deadlines and assign tasks to team members if applicable.
- Track content publishing or last updated date.
4. Consider Content Distribution
Content distribution involves promoting your content across various channels to reach a broader audience.
To do this, you will need to identify the most effective distribution channels for your niche and audience, such as:
- Social media platforms (e.g., Facebook, Pinterest, Instagram, etc.)
- Email marketing campaigns
- Guest posting on relevant websites or blogs
- Collaborating with influencers or industry experts
- Utilizing paid advertising, such as Google Ads or sponsored social media posts
Then you will need to repurpose the content for each platform. This is important as every platform has its own best practices to perform well.
For example, continuing with the same example, you can repurpose your recipes for Instagram by creating visually appealing images and posting a carousel of images showing step-by-step instructions.
Then you can create a video tutorial and share it across Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram, as well as embed it on the website. You could also send an email campaign to your email list (you should consider building one if you don’t have one) with a blog post featuring the recipe and a link back to all the other platforms.
This is a very basic example, but I hope it makes the point. In reality, the possibilities are endless.
5. Create a Content Optimization Plan
A content optimization plan is a cadence of analysis and optimization activities that you should perform regularly.
Optimizing your content for search engines is an ongoing process. To maintain and continuously improve search engine rankings, you will need to create and follow a content optimization plan.
The specific activities depend on the type of content and internal processes, but I will give you a few examples.
Here are some tasks for a content optimization plan with suggested frequencies:
- Analyze rankings (monthly): Monitor your keyword rankings to identify opportunities for improvement.
- Prioritize content for optimization (monthly): Based on your current ranking analysis prioritize pages for content optimization. Prioritize the content that has the highest potential to generate traffic and/or conversions.
- Optimize for featured snippets (monthly): Identify relevant keywords ranking in the top 5 for which you can provide concise, direct answers. Structure your content to cater to these snippets by using headers, bullet points, and clear formatting.
- Optimize titles and meta descriptions (monthly): Regularly review and optimize the titles and meta descriptions of your web pages. Focus on improving click-through rates (CTR) by crafting enticing and descriptive titles and meta descriptions.
- Perform content configuration (quarterly): Every three months, review the search queries in Google Search Console. Depending on the search query analysis and content analysis, add missing keywords, improve topical coverage, and ensure the content is comprehensive and up to date. Consider incorporating new information or addressing any gaps in the existing content.
- Improve internal linking (quarterly): Periodically assess your internal linking structure to ensure it is optimized for both user experience and search engine crawlers. Identify opportunities to link relevant pages together within your website, using descriptive anchor texts.
- Monitor and analyze user engagement metrics (quarterly): Keep an eye on user engagement metrics such as bounce rate, time on page, and conversion rates. Analyze these metrics to identify areas of improvement and make adjustments to your content accordingly.
- Update content significantly (every 6 – 9 months): Don’t forget about more significant updates to your content. This involves revisiting the structure, formatting, and overall messaging. Consider incorporating new research, case studies, statistics, or any relevant information that can enhance the value of the content compared to the old content and the competition.
6. Analyze and Re-Assess Your Strategy
Regularly monitor and analyze the performance of your content strategy to track progress toward your goals and identify areas for improvement.
Evaluating your SEO strategy helps you make data-driven decisions and optimize your content’s impact.
Consider following these key steps:
- Gather and analyze data: Utilize analytics tools to track your defined content strategy goals.
- Compare against goals: Assess if your strategy is on track to achieve objectives or needs adjustments.
- Identify successful content: Find patterns among high-performing content and use insights for future content creation.
- Evaluate underperforming content: Determine reasons for underperformance and decide whether optimization or removal is necessary.
- Seek feedback: Engage with your audience, collect insights, and tailor content to their needs.
- Adjust and optimize: Refine your strategy based on analysis, trends, and feedback.
- Stay updated: Stay informed about industry trends, competitors, and search engine algorithms.
- Set and follow review and optimization cycles: Schedule regular intervals to review and optimize your strategy. This could be quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, depending on the scope and resources available.
There you have it!
By following these steps and tips outlined in the article you can get started with creating effective SEO content that attracts organic traffic, resonates with the target audience, and improves search engine rankings.