On-Page SEO Optimization: The Beginner’s Guide
Updated:
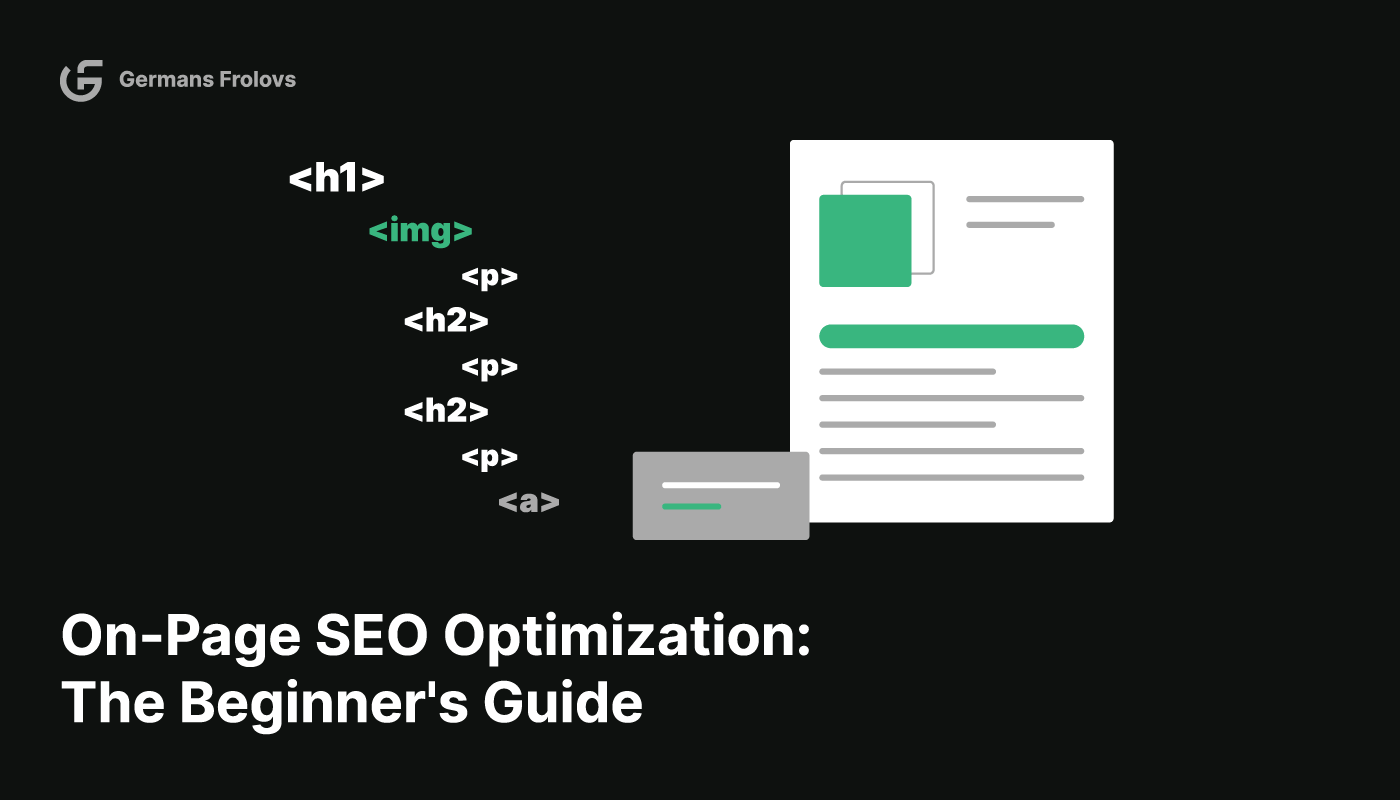
On-page SEO is a critical component of search engine optimization, focusing on optimizing various website elements, such as content, title tags, metadata, URL structure, and more. By doing so, websites can appear more relevant to user search intent and consequently rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs), increasing visibility and traffic.
Key factors to consider for on-page SEO include title tags, meta descriptions, H1 tags, heading tags, images, keywords, content, mobile-friendliness, and user engagement elements.
Implementing advanced tactics such as targeting featured snippets, using schema markup, and improving page speed can further enhance visibility on the SERP.
A successful SEO strategy combines on-page and off-page SEO to establish a solid foundation for higher rankings and overall user satisfaction.
Table of Contents
- What Is On-Page SEO?
- Why Is On-Page SEO Important?
- What On-Page SEO Factors Should I Optimize?
- How to Do On-Page SEO Optimization?
- What Are Some Advanced On-Page SEO Tactics?
- How to Evaluate Your On-Page Optimization?
- How to Analyze a Competitor’s On-Page SEO?
- What is the Difference Between On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO?
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO (sometimes called on-site SEO) refers to the process of optimizing elements on your web pages to rank higher in search results and get more search engine traffic.
This optimization includes configuring on-page content, title tags, internal links, and more.
Search engines like Google assess keywords and other on-page factors to determine whether a page matches a user’s search intent. If a page is deemed relevant and useful, it will appear higher in search results.
Why Is On-Page SEO Important?
On-page SEO is an essential part of search engine optimization (SEO) because search engines use keywords and other on-page elements to determine whether a page matches a user’s search intent.
A well-optimized page is more likely to be considered relevant and helpful and subsequently be ranked higher in search results.
Google continuously prioritizes user experience, so creating valuable content that aligns with user intent is more crucial than ever.
What On-Page SEO Factors Should I Optimize?
On-page SEO factors you should focus on are listed below:
- Title Tags
- Meta Descriptions
- H1 Tags
- Heading Tags
- URL Structure
- Images
- Keywords
- Content
- Internal Links
- External Links
- Expertise Display
- Mobile-Friendliness
- User Engagement Elements
- Geo-Targeting Elements (for Local SEO)
- Schema Markup
Read on to learn how to do on-page optimization for each of these on-page SEO factors with examples.
How to Do On-Page SEO Optimization?
Now that you know the basics and are ready to learn more about how to optimize your on-page SEO, let’s dive into each element (and others) in greater detail.
1. Optimize Title Tags
Title tags are pieces of HTML code that indicate a page’s title.
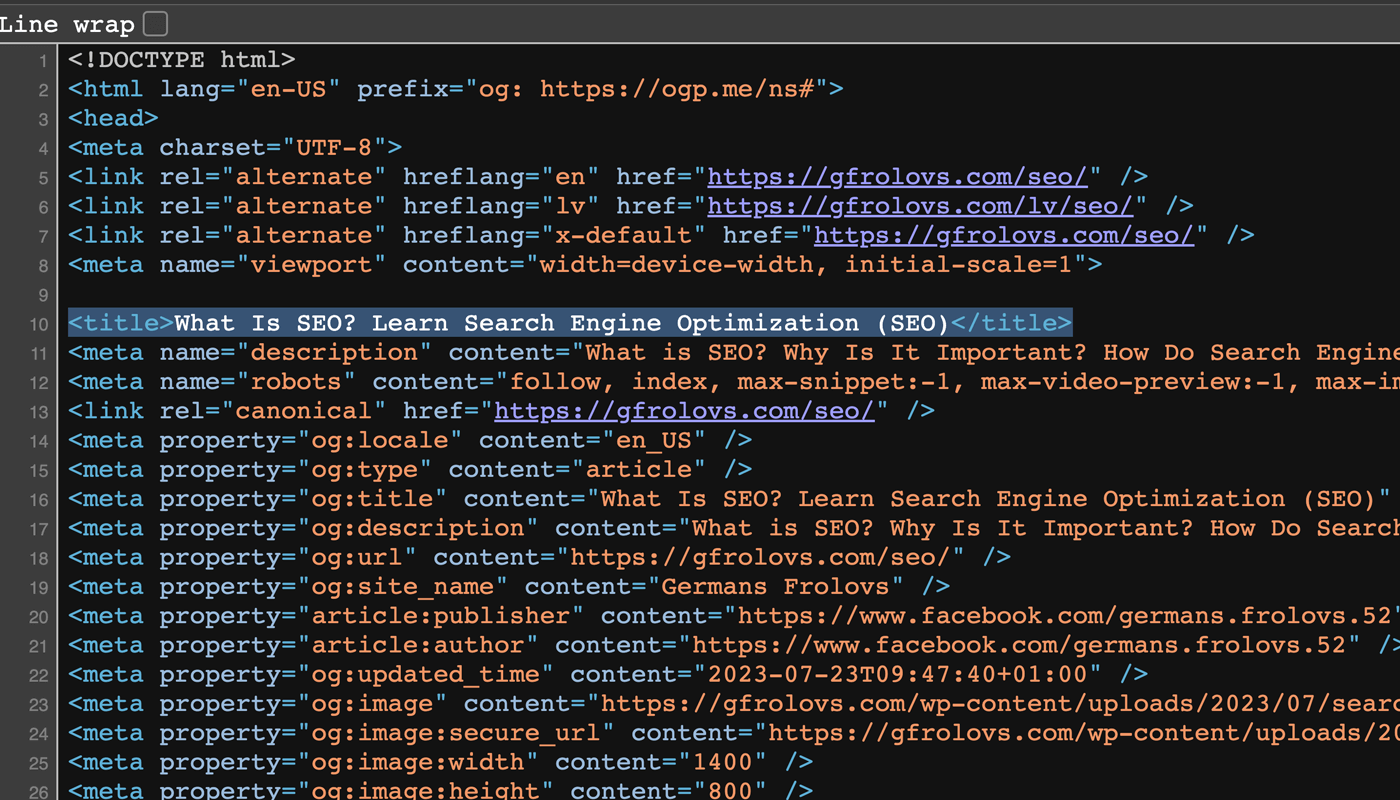
Title tags are displayed in search engines, social media posts, and browser tabs.
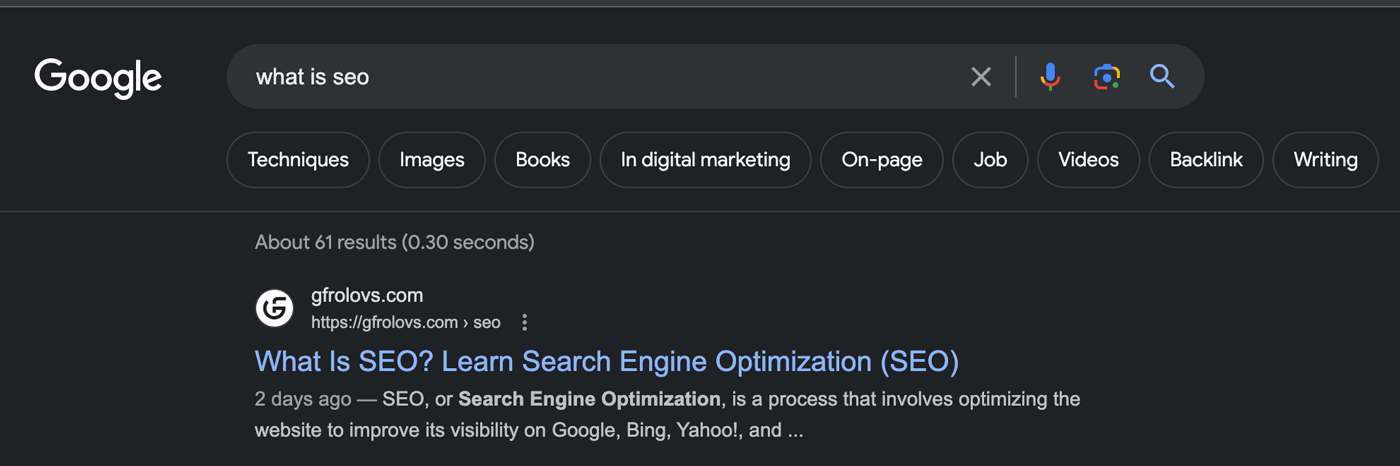
Create brief yet descriptive title tags of 50-60 characters that include your target keyword (without keyword-stuffing), preferably as close to the beginning as possible.
Here are examples of a good title tag and a poorly written title tag:
- Good title tag: “Luxury Car Rentals in London | Exquisite Fleet of High-End Vehicles”
- Poorly written title tag: “Car Rentals | Luxury Cars | Rent a Car”
You also need to ensure that each page has its own unique title tag to avoid any potential cannibalization.
You can use tools like Google SERP Simulator by Mangools to test how your titles will appear in search engine results pages (SERPs) and whether they fit within the title length limit.
2. Write Engaging Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions provide a summary of your web page’s content and show up on search engine results pages.
In the HTML code, it is typically placed below the title tag.
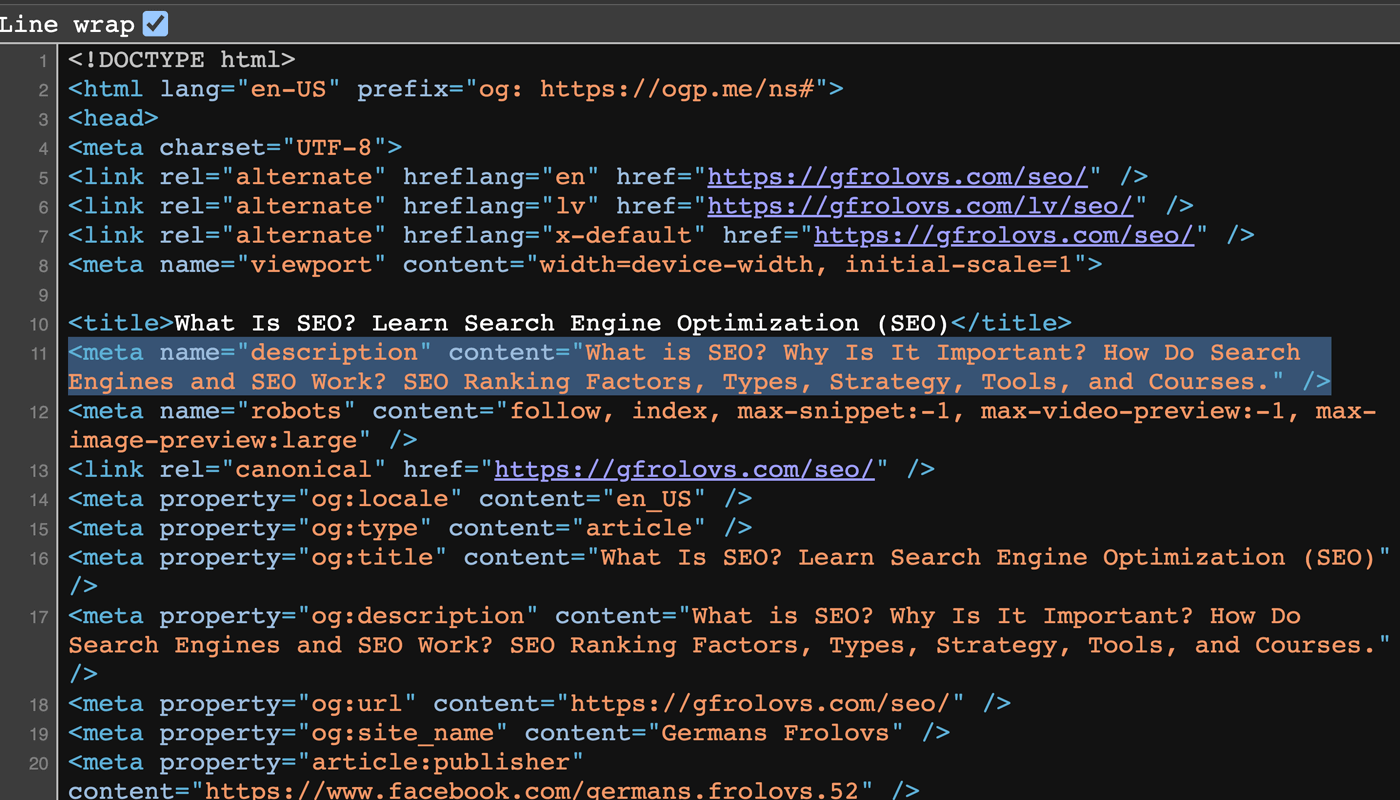
Craft concise meta descriptions that include your target keyword in an active voice while considering the character limit of 160 characters.
Focus on writing compelling meta descriptions that accurately describe your page’s content and persuade users to click through by using a call-to-action (CTA) phrase.
Here are examples of good and bad meta descriptions:
- Good meta description: “Rent the latest luxury cars from our fleet in London. We specialize in providing exquisite vehicles for special occasions.”
- Bad meta description: “Luxury car rentals in London. Rent a car today!”
Pay attention to using keywords naturally and avoid keyword stuffing.
You can use the same tool (SERP Simulator by Mangools) to test how meta descriptions will appear in search engine results pages and ensure they fit within the length limit.
3. Optimize H1 Tags
The H1 tag is an HTML element that indicates the main heading of a web page.
H1 tags are essential for search engine crawlers to understand what the page is about. Since H1 tags serve as the main headline, make sure to include your target keyword for additional context.
Ensure that these tags are unique for each page and have one H1 tag per page.
I recommend keeping your H1 tags the same as your title tags. Especially since Google started to rewrite titles in SERPs in August 2021.
Instead of displaying the original title tags, Google often replaces them with “other relevant text from a webpage.” In many cases, Google utilizes the content from a page’s H1 tag as a replacement.
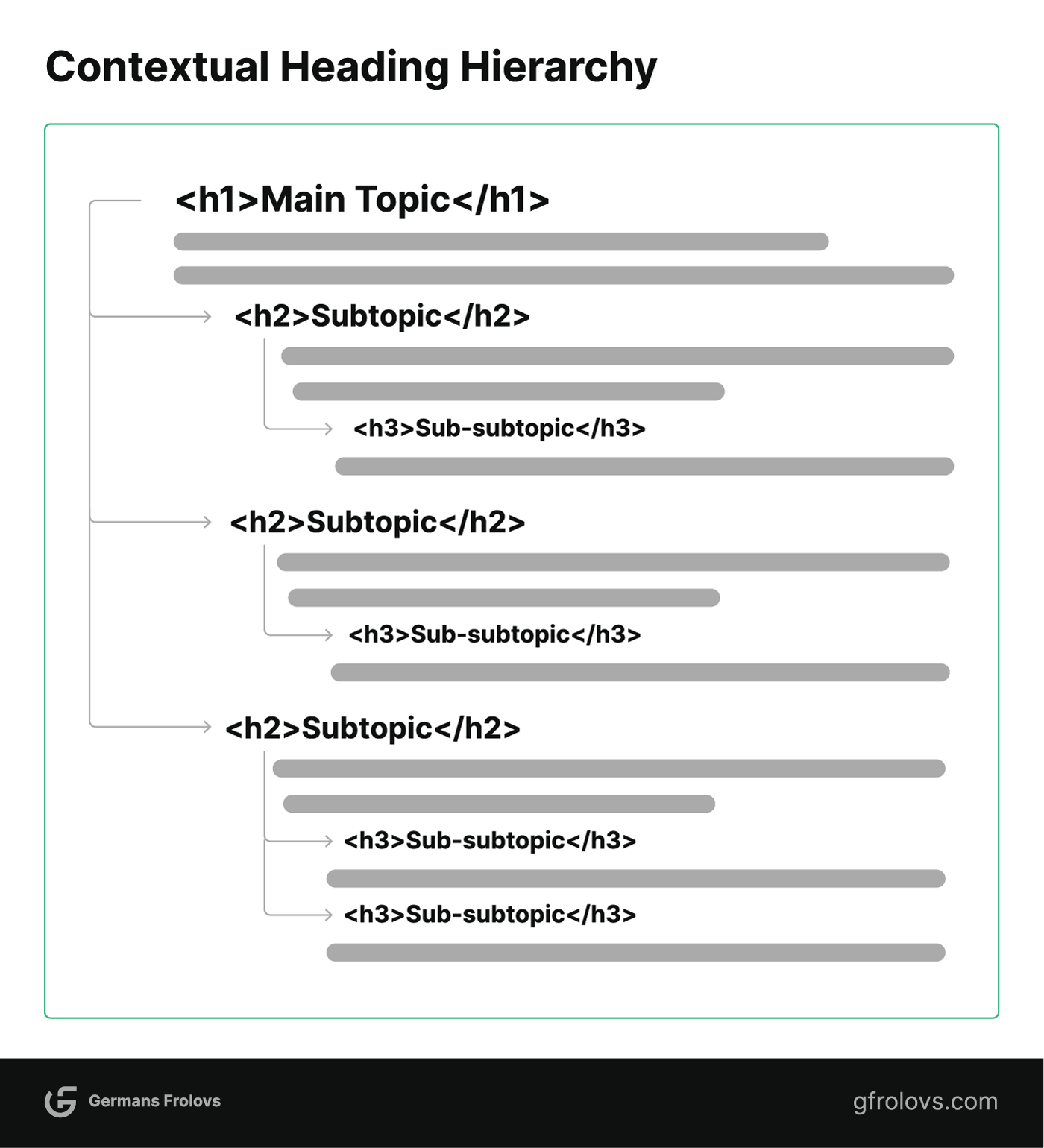
4. Use Heading Tags to Structure Your Page
Heading tags are HTML elements used to define the headings and subheadings on a web page.
You should organize your content in a logical hierarchy with headings (H2-H6).
This makes it easier for readers and search engine crawlers to better understand the structure of your web page.
Include keywords in your headings too. However, make sure not to keyword stuff by using them excessively or out of context.
It’s essential to pay attention to creating a well-structured layout that breaks up content into sections. Readers should be able to find their way around a page without any difficulty.
Solid structure for a web page about “Best Large Luxury Cars For 2023” is illustrated below.
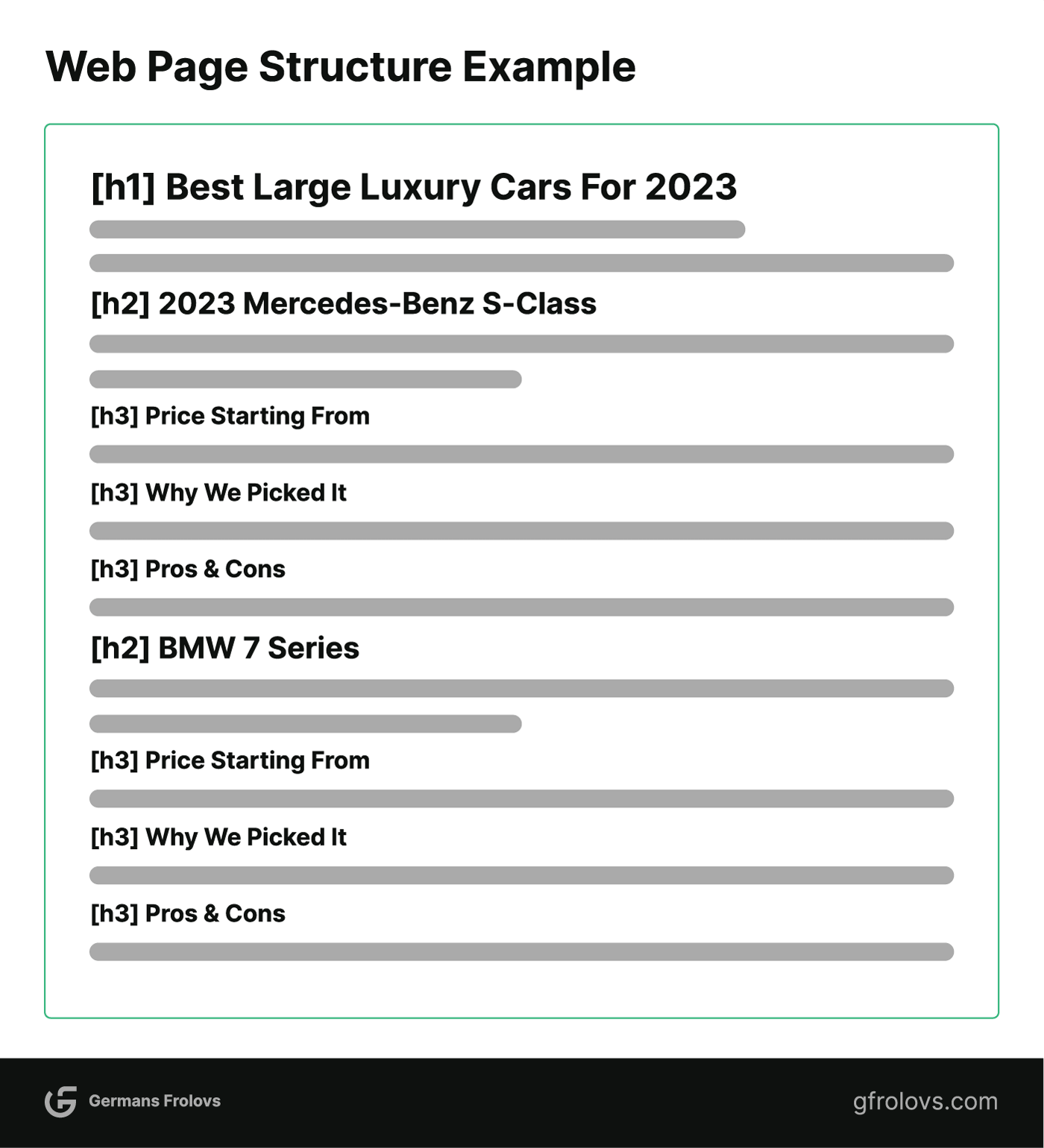
To optimize your web page’s structure start by using the H1 tag as your page title or headline, capturing the main context of your content.
For subtopics, incorporate H2 tags, providing a clear hierarchy and contextual flow.
If additional subheadings are necessary for more in-depth coverage, utilize H3, H4, and so on. It is crucial to ensure that these subheadings remain relevant to your primary keyword and effectively cover related subtopics, enhancing the overall coherence and relevance of your content.
5. Optimize URL Structure
URLs are the web addresses of your pages, which people use to access them.
When web crawlers visit a webpage, the first things they process are the URLs.
The importance of providing contextual information to Google cannot be understated. The more context Google has about a specific page, the better its understanding becomes.
Make sure your URLs are keyword-rich, descriptive, simple, and short.
Avoid overly long or confusing URLs that make finding a particular page difficult for both users and search engine crawlers.
It is also essential to use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) when separating words in the URL string as they are easier to read for humans and search engines alike.
Below are examples of a good URL structure and a bad URL structure for a website about luxury cars in the UK that also offers car rentals:
- Good URL structure: www.domain.com/luxury-cars/rentals/london/
- Poor URL structure: www.domain.com/luxury_carrentalslondon
6. Include and Optimize Images
Images add an extra layer of interactivity to your web pages and can help break up large chunks of text.
Make sure to include relevant images in your content that are properly optimized for SEO purposes.
Image optimization involves:
- Properly sizing the images: Size images to the exact dimensions necessary, as larger sizes can slow down the page loading speed.
- Compressing file sizes: Use free tools like TinyPNG/JPG to reduce the file size by compressing the image files without sacrificing quality.
- Writing descriptive file names: Keep file names short, and descriptive, and include your target keyword. For example, the featured image file name for an article about the “Best Luxury Cars of 2023” showing cars with their placings could be “luxury-car-rank-2023.jpg.”
- Writing descriptive alt text: Use descriptive words and phrases to describe the contents of images, while also including your target keyword. For instance, the alt text for the same image could be “Luxury car ranking for 2023”.
- Writing descriptive captions and surrounding text: Include descriptive text both above and below images, since Google learns about the contents of the page through not only image file names but also captions and the text surrounding it.
7. Place Keywords Strategically
It’s important to keep your target keyword in mind when creating content.
You should incorporate your focus keyword into the most prominent locations on a web page. As mentioned in a few prior examples these “prominent locations” include:
- The page title and H1 tag
- Meta description
- Headings (H2-H6)
- Image ALT tags, file names, and captions
- At the beginning of your page content
Additionally, you should use the primary keyword naturally throughout the body of your page content as well as incorporate related terms and phrases.
When it comes to SEO, contextual relevancy is essential.
Utilize related keywords that make sense and flow naturally in your content to add more context and comprehensiveness that helps cover the topic in depth.
8. Write High-Quality Content
The most important step you should take when creating high-quality SEO-optimized content is matching the user’s search intent.
What does the user want to learn or find in response to their search query?
The answer to this question is your target keyword’s search intent. You can identify it by searching for the keyword in Google and looking at the top search results.
Your content should fulfill that intent. If it doesn’t, then chances are your page won’t rank well in search engine result pages.
When you write content, focus on fulfilling the user’s need and providing them with value. Google in turn will reward your page with higher rankings.
To create the best content possible, aim to write comprehensive and informative pieces that cover topics in-depth.
There are many other aspects that must be considered and deserve a separate article, but the following best practices should help you get started:
- Ensure the content matches user intent.
- Make the content easy to read and understand by using simple language, short sentences, and paragraphs.
- Use keywords in a natural and contextual manner.
- Write unique content that adds value.
- Fully answer the user’s query as definitively and quickly as possible so the users don’t have to search elsewhere.
- Incorporate multimedia like images, videos, and infographics to make the content more interesting and engaging.
- Update content regularly so that it remains relevant.
9. Add Internal Links
Internal links connect one page to another page within the same website.
Internal links help search engine crawlers navigate and crawl your pages more efficiently while also helping users find additional relevant content on your site.
You should link to related pages on your website in order to add more context and relevance. This will also help reduce bounce rates by keeping users engaged with your content for longer periods.
When creating internal links, be sure to use descriptive anchor text that accurately describes the linked page’s contents. This will help Google understand the content of the linked page and can improve its rankings as well.
To give an example here is a good and a poor internal link anchor text:
Example 1 (poor internal link anchor text):
- “At our luxury car dealership, we offer a wide range of exquisite vehicles for you to choose from. If you’re interested in learning more about our collection, you can click here to explore further.”
Example 2 (good internal link anchor text):
- “At our luxury car dealership, we offer a wide range of exquisite vehicles for you to choose from. If you’re interested in exploring our collection of luxury sports cars, you can explore our collection of luxury sports cars to find the perfect combination of performance and elegance.”
10. Include External Links
External links are links pointing to other sites outside of your website.
You should include external links in your content when it adds value and relevance to the topic being discussed.
For example, if you’re writing an article about the “Best Luxury Cars of 2023” you could link to various car reviews from other websites.
Links to authoritative external sources are a great way to provide value to your users and add more context and credibility to your content.
11. Display Expertise
Google rewards websites that show a high level of expertise on a given topic.
Here are some ways Google advises site owners to display expertise:
- Display that you know the topic well.
- Create content with factual information backed up by reliable sources, visible to both crawlers and users.
- Provide information about the author and contributors of the content. For example, include links to an “author” page or an “about us” page that provides information about the website’s author, contributor(s), or organization.
- Ensure the content does not contain any easily-verified factual errors.
12. Consider Mobile-Friendliness
With the increasing number of mobile users, Google now considers a website’s mobile-friendliness or responsiveness when ranking it.
You should make sure your website is optimized for both desktop and mobile devices.
Make sure your page content can be viewed easily on any device size by testing your pages on different screen sizes using various tools such as Chrome DevTools or Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
13. Optimize for User Engagement
It’s important to go beyond just attracting visitors and focus on enhancing their overall interaction with your content.
Here are some strategies and examples to encourage meaningful user engagement:
- Provide valuable content: Offer truly useful and valuable content that keeps users engaged.
- Use headings and subheadings: Break your content into logical sections using clear and descriptive headings and subheadings.
- Include a clickable table of content: Add a table of contents with jump links that allow users to quickly refer to the portion of content relevant to them.
- Incorporate relevant CTAs: Call-to-action (CTA) buttons or links are effective in guiding users to take desired actions. For example, for a luxury car website, you can use CTAs like “Schedule a Test Drive,” “Request a Quote,” or “Explore Financing Options” to encourage users to further engage with your dealership.
- Engage with multimedia: Enhance user engagement by incorporating visually appealing multimedia elements. Include high-resolution images and illustrations, as well as videos.
- Offer interactive tools: Provide interactive tools such as calculators to assist users in making informed decisions or completing tasks.
14. Optimize for Social Sharing
Social media is a great way to promote your content and boost traffic to your website.
You should make it easy for visitors to share your content on various social networks such as Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and others by adding social sharing buttons. Make sure the buttons are prominently displayed so users can quickly locate them.
You should also include open graph meta tags in order to ensure that when users share your content on social media, it displays properly with a featured image, title, description, etc. This will help you get more visibility and traffic from social media platforms.
15. Optimize for Local Search
If your business or website caters to local customers, then optimizing for local search is essential.
Google and other search engines consider various signals when ranking websites for local search queries.
Here are some techniques that can help you rank higher for local searches:
- Optimize local listings, citations, and NAP consistency: Ensure consistency in your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) across local directories and listings.
- Optimize local content: Incorporate location-specific keywords into your content to cater to “near me” searches. Create relevant and engaging location-based content.
- Build local links: Establish partnerships and collaborations with local businesses and organizations to gain reputable backlinks and enhance your website’s local relevance and authority.
What Are Some Advanced On-Page SEO Tactics?
While the above techniques form the basics of on-page SEO, there are multiple advanced tactics you can use to take your optimization efforts to the next level.
Target Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are short snippets of text that appear at the top of the search engine result page (SERP). A featured snippet aims to answer the searcher’s question with a short answer format.
By having your content featured in a snippet, you can significantly boost the visibility on the SERP.
Featured snippets can be in a form of a paragraph, list, table, or video.
Google takes these snippets from webpages that rank in the top 10 positions for a given keyword. To maximize your chances of appearing in a featured snippet, your page must rank on the first page.
To find featured snippets opportunities you can use free Ahrefs Webmaster tools – specifically Ahrefs’ Organic Keyword Report.
Simply open up the report for your site, filter for the top 10 rankings, and where you don’t own the featured snippet.
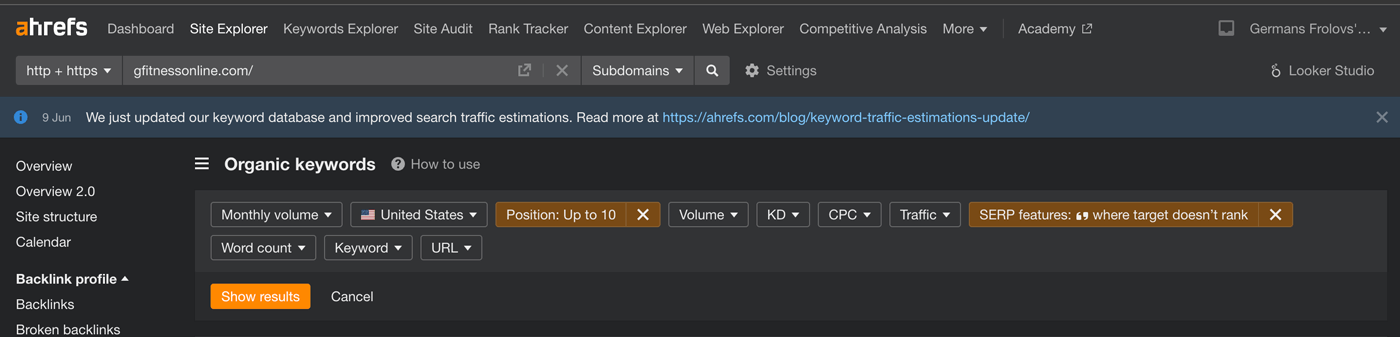
To optimize your content for featured snippets, format your content according to the snippet type. Check who is currently owning that featured snippet, follow the same structure but make the content more helpful, clear, and informative.
Here are some guidelines you can follow depending on the featured snippet type:
- Paragraph snippets: Structure your answer with a heading and short paragraph (max 350 characters). The paragraph should directly answer the question by echoing it back. The answer should also include facts and numbers if possible.
- List snippets: Include a numbered or bulleted list, or use H2 or H3 headings.
- Table snippets: Format information into rows and columns under headings.
- Video snippets: Embed relevant videos on pages. It’s also recommended that you add transcripts/captions to the video.
Get Rich Snippets with Schema Markup
Schema markup is a type of code that helps search engines understand what your content is about. It can also help your content appear more prominently on the SERP by providing additional information like ratings, prices, availability, etc.
Example of a product schema markup using JSON-LD for a fictional laptop product is presented below.
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Example Laptop X200",
"image": [
"https://example.com/images/laptop-x200-front.jpg",
"https://example.com/images/laptop-x200-back.jpg"
],
"description": "The Example Laptop X200 is a powerful and lightweight laptop designed for productivity and entertainment.",
"sku": "EXMPLT-X200-BLK",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "Example Electronics"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.5",
"reviewCount": "32"
},
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "999.99",
"priceValidUntil": "2023-12-31",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock",
"seller": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Example Store"
}
},
"review": [
{
"@type": "Review",
"reviewRating": {
"@type": "Rating",
"ratingValue": "4.5",
"bestRating": "5",
"worstRating": "1"
},
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "John Doe"
},
"datePublished": "2023-06-15",
"reviewBody": "I love this laptop! It's fast, has a great display, and the battery life is impressive."
},
{
"@type": "Review",
"reviewRating": {
"@type": "Rating",
"ratingValue": "4.0",
"bestRating": "5",
"worstRating": "1"
},
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Jane Smith"
},
"datePublished": "2023-07-01",
"reviewBody": "The Example Laptop X200 is a solid choice for anyone in need of a reliable and capable laptop."
}
]
}
</script>Consider leveraging structured data using relevant schema types to improve click-through rate and visibility on SERPs.
The above example uses product schema markup, but you can add many different types to your pages.
Common types of schema markup include:
- Organization
- Person
- Local Business
- Product & Offer (like the one featured above)
- Breadcrumbs
- Article
- Video
- Event
- Recipe
- And more
You can use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or Schema Generator tools to generate appropriate schema markups.
Optimize for Page Speed
Page speed is an important factor for user experience and also plays a role in website ranking. While it may not be a direct on-page SEO element, it is closely interconnected with various on-page SEO factors.
If your pages take more than 3 seconds to load, there’s serious room for improvement.
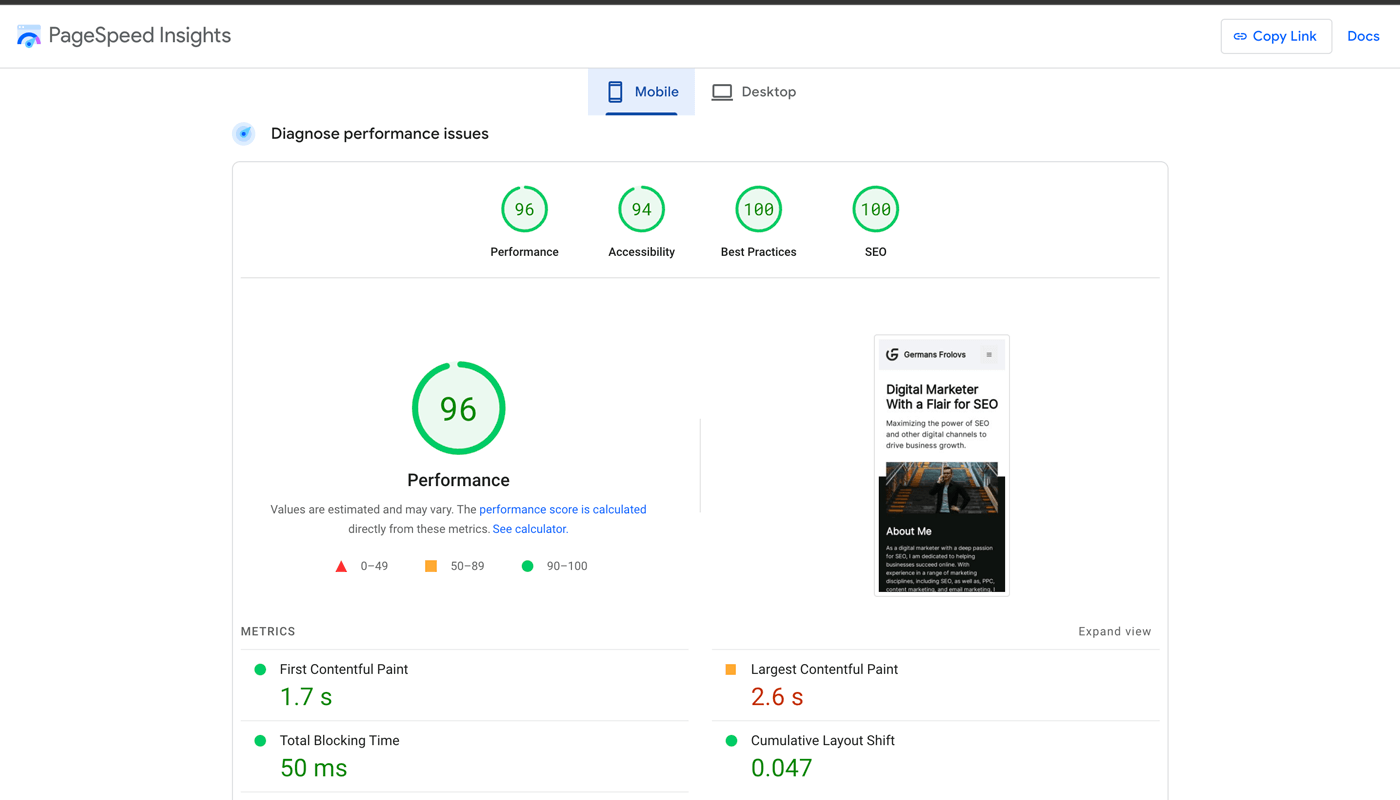
Google PageSpeed Insights is a great tool to use to measure page loading time and get recommendations on how to improve it.
This tool assesses Google’s Core Web Vitals, which are essential metrics that evaluate the user experience of a website’s performance.
Comprising three key factors, they influence search result rankings on Google. But to a very small degree.
The three Core Web Vitals encompass:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the speed at which the primary content of a webpage is displayed to users.
- First Input Delay (FID): Determines how quickly a webpage responds to user interactions.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Gauges the stability of a webpage’s layout by assessing the occurrence of unexpected content shifts after rendering.
It is noteworthy that the First Input Delay (FID) metric will be replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP) in March 2024.
Google has established specific thresholds for each Core Web Vital, categorizing them as “Good,” “Needs Improvement,” or “Poor,” which aids in assessing their performance quality.
How to Evaluate Your On-Page Optimization?
To assess your on-page optimization effectively, you’ll need to utilize specialized SEO tools or conduct manual evaluations using comprehensive checklists.
By premium using tools like Clearscope, Surfer, or Page Optimizer Pro, you can gain valuable insights into your website’s performance regarding content and make data-driven improvements.
Additionally, manual assessments with checklists can help you thoroughly evaluate your on-page SEO.
How to Analyze a Competitor’s On-Page SEO?
You can analyze a competitor’s on-page SEO through either manual analysis using an on-page SEO audit checklist or using on-page SEO optimization tools.
For manual analysis, visit your competitor’s websites and closely examine their on-page elements, content, and overall structure using checklists to guide your audit. Take note of patterns and strategies you observe.
Alternatively, utilize on-page SEO optimization tools like Clearscope, Surfer, Page Optimizer Pro, and others. These tools provide in-depth analysis and insights into your competitor’s on-page optimization, including keyword usage, topical coverage, and more.
The manual analysis allows personal exploration and understanding, while on-page SEO tools provide comprehensive data and insights.
What is the Difference Between On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO?
The main difference between on-page SEO and off-page SEO is that on-page SEO focuses on optimizing the elements of a webpage, while off-page SEO focuses on actions taken outside the webpage to impact its rankings.
On-page SEO involves optimizing elements within your website, such as content, title tags, internal links, and many others.
On the other hand, off-page SEO optimization covers actions outside your website, such as acquiring backlinks, optimizing social media presence, and utilizing public relations efforts.
Both on-page and off-page SEO are vital components of a comprehensive SEO strategy, with on-page SEO factors being more controllable and essential for laying a strong foundation for off-page efforts.