Technical SEO: The Beginner-Friendly Guide
Updated:

Technical SEO is a crucial aspect of website optimization that focuses on improving the website’s infrastructure and underlying elements to enhance its discoverability and understanding by search engines.
This process involves several key elements including crawlability, indexability, accessibility, rankability, and clickability. Each of these elements plays a critical role in ensuring that a website is easily accessible, comprehensible, and appealing to both search engines and users.
Crawlability and indexability are foundational elements of technical SEO that ensure a website can be discovered, accessed, and included in a search engine’s index. Accessibility, on the other hand, ensures that a website is usable, understandable, and perceivable by a diverse range of users.
Rankability and Clickability are the final stages of technical SEO that focus on enhancing a webpage’s potential to achieve higher positions in search engine rankings and attract user clicks in search engine result pages (SERPs).
To achieve technical SEO success, one must adhere to the various best practices listed in this article.
Table of Contents
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO refers to the process of optimizing a website’s infrastructure and underlying elements to help search engines like Google discover, crawl, understand, and index web pages.
Technical SEO is a part of the larger search engine optimization (SEO) process and an important foundational element for successful SEO.
Why is Technical SEO Important?
Technical SEO is essential for a website’s success in search engine rankings and visibility. Even if you produce excellent content, neglecting the necessary measures to enable search engine bots to crawl and comprehend your website can undermine the benefits of your efforts.
Technical SEO is the foundation of your website, like a blueprint for a mansion. It ensures easy access for search engines to explore and showcase your valuable content. Without it, your website remains hidden, preventing visitors and search engines from appreciating its treasures. By investing in technical SEO, you create clear paths for search engine bots to navigate and your content to reach its intended audience.
That is just one simple example of why technical SEO is so important. Let’s now look at the major elements involved in technical SEO.
What Are the Technical SEO Elements?
Technical SEO can be broken down into five distinct elements:
- Crawlability
- Indexability
- Accessibility
- Rankability
- Clickability
These five elements and their place in the technical SEO hierarchy are best illustrated in OnCrawl’s blog post on Search Engine Land using a renowned Maslov’s Hierarchy of Needs but re-done for search engine optimization.
Simply put, if needs in the lower levels of the hierarchy are not met, it is impossible to reach the higher ones.
For example, if your website is not even crawlable and indexable by search engine bots, then your efforts in ensuring clickability through for example structured data implementation will be in vain.
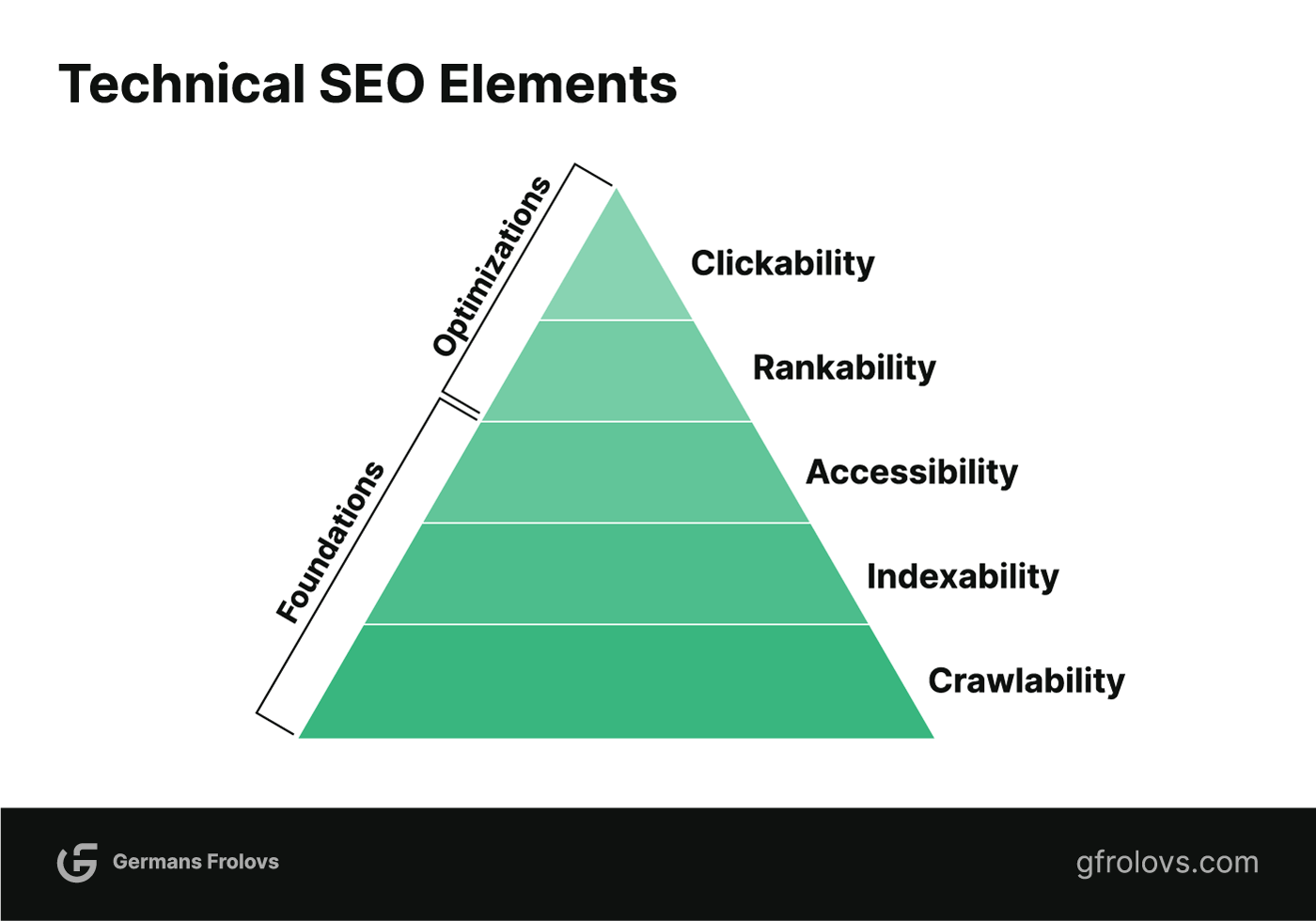
What is Crawling?
Crawlability refers to a URL’s ability to be discovered and accessed by search engine bots. It is essential to ensure that the web pages you want to rank on search engines are easily accessible.
Crawlability is a foundational element in the hierarchy of technical SEO.
Crawling happens when search engine bots access and process content from the web by following links. Crawlable URLs are not forbidden to search bots and are known to search engines.
The most common way to control what gets crawled on your website is to utilize a robots.txt file to specify where search engines can and cannot go on your site.
NOTE
Google may still index pages it can’t crawl in cases when links are pointing to them.
For instance, let’s say you have a “top-secret page” on your website that you don’t want search engine bots to crawl. This page could contain confidential information, exclusive content for members, or other sensitive data that you’d like to keep hidden. To ensure that search engine bots don’t crawl this “top-secret page”, you’ll need to add a specific directive in your website’s robots.txt file.
A robots.txt file is a plain text file placed in the root directory of your website and acts as a guide for search engine bots, specifying which areas of your site they are allowed or disallowed from crawling. By including a “Disallow” directive in your robots.txt file, you can effectively instruct search engine bots not to crawl the specified URL.
In the case of your “top-secret page”, you would add the following directive to your robots.txt file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /top-secret-page/This directive consists of two lines:
- The User-agent: * line indicates that the following rules apply to all search engine bots (denoted by the asterisk). If you wish to target a specific bot, you can replace the asterisk with the name of the bot, for example, “User-agent: Googlebot”.
- The Disallow: /top-secret-page/ line specifies the URL path that search engine bots cannot crawl. This should be the relative URL path of your “top-secret page.”
There are many other ways to control and optimize the crawlability of your website. For example, implementing access restrictions via login systems or only allowing specific IP addresses to access specific web pages.
To optimize crawlability you could maximize the crawl budget, create and optimize the XML sitemap, optimize site architecture, URL structure, and more. All of these are a part of optimizing your website for crawlability.
What is Indexability?
Indexability refers to the ability of a webpage to be included in a search engine’s index.
A search engine’s index is essentially a database of pages available for display in search results.
To check if a page is indexed, simply enter “site: [page URL]” into Google search and see what happens.
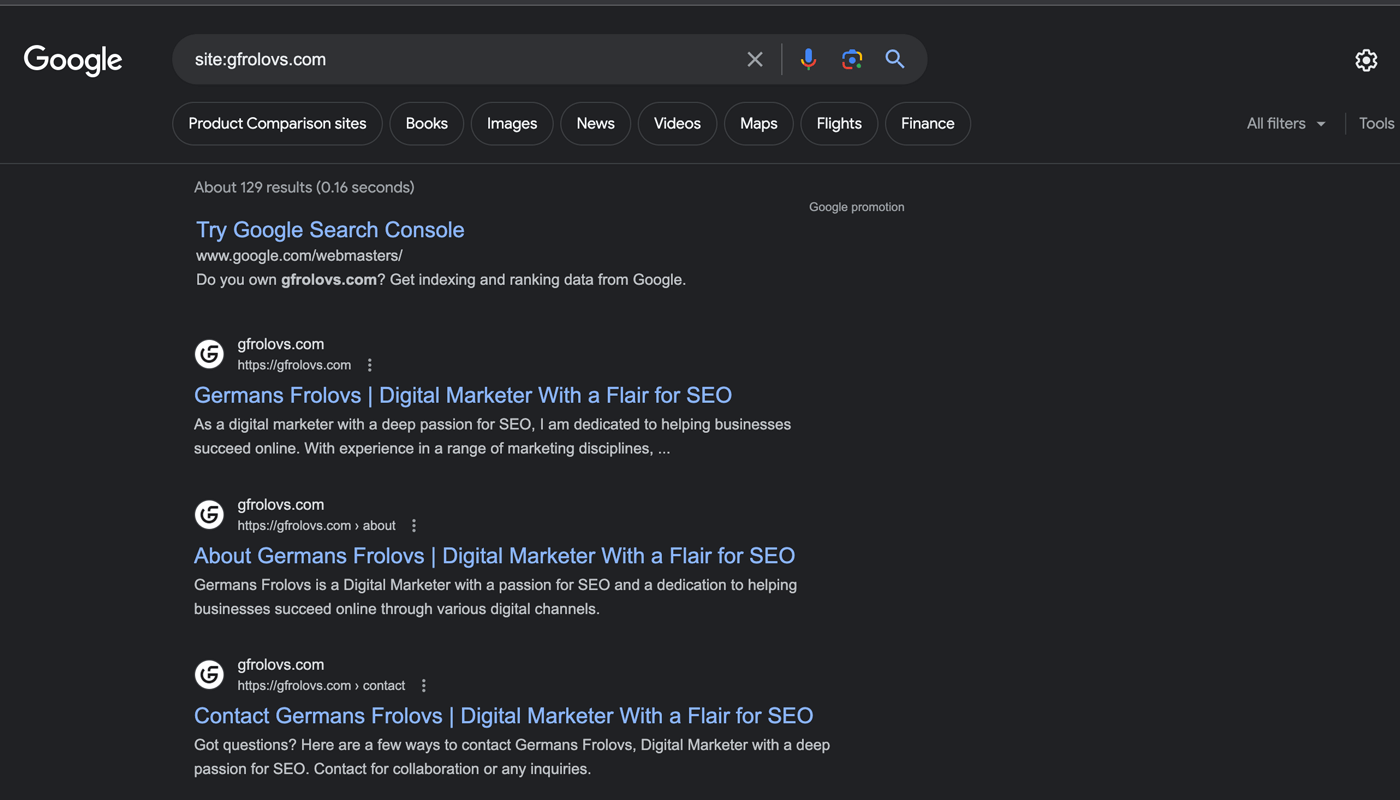
If the page appears in the search results, then it has been successfully indexed by Google.
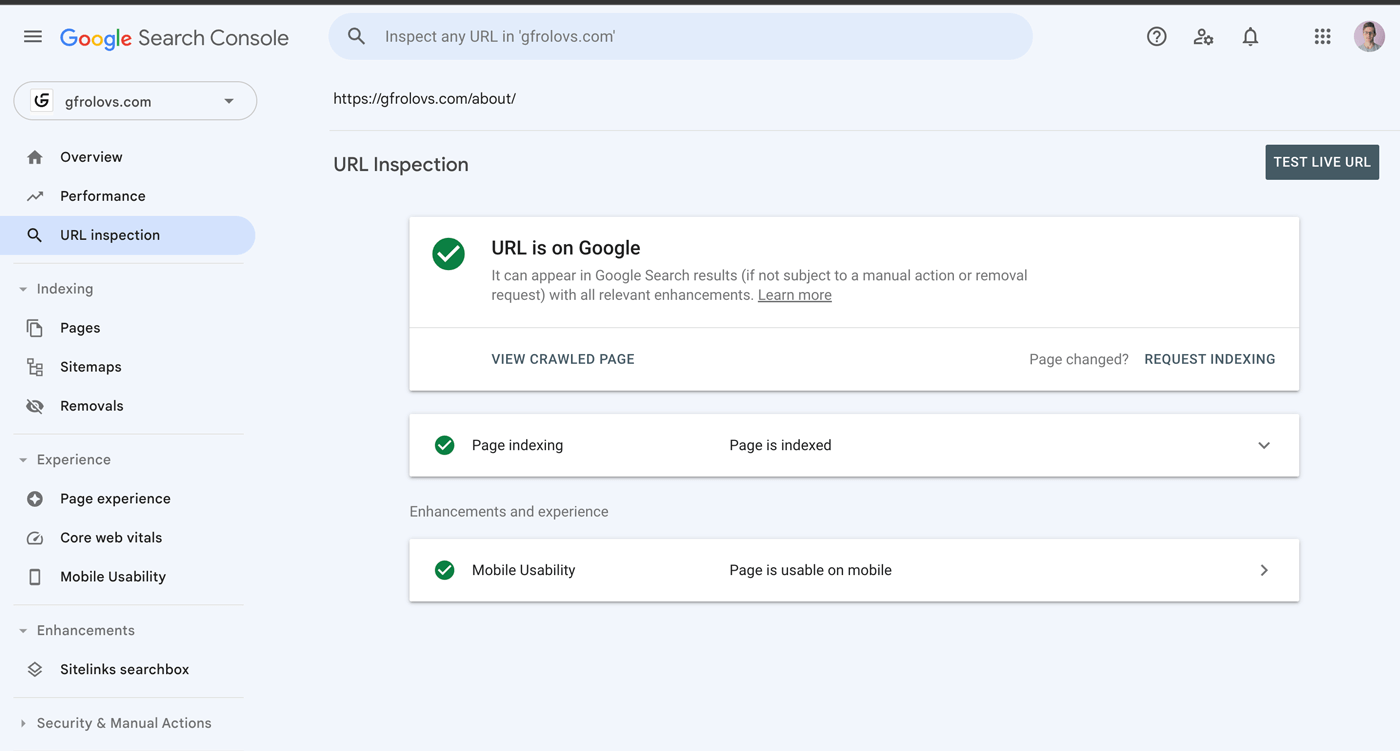
Alternatively, you can use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to check whether a URL is indexed and obtain more detailed information.
There are a few things that can keep a page from being indexed.
Most commonly, it is the “noindex” tag implemented on the page.
It’s an HTML snippet that instructs search engine bots not to index the page, placed within the <head> section of your webpage.
You can check if this tag has been applied to your page by viewing the source code of your page and searching for “noindex”.
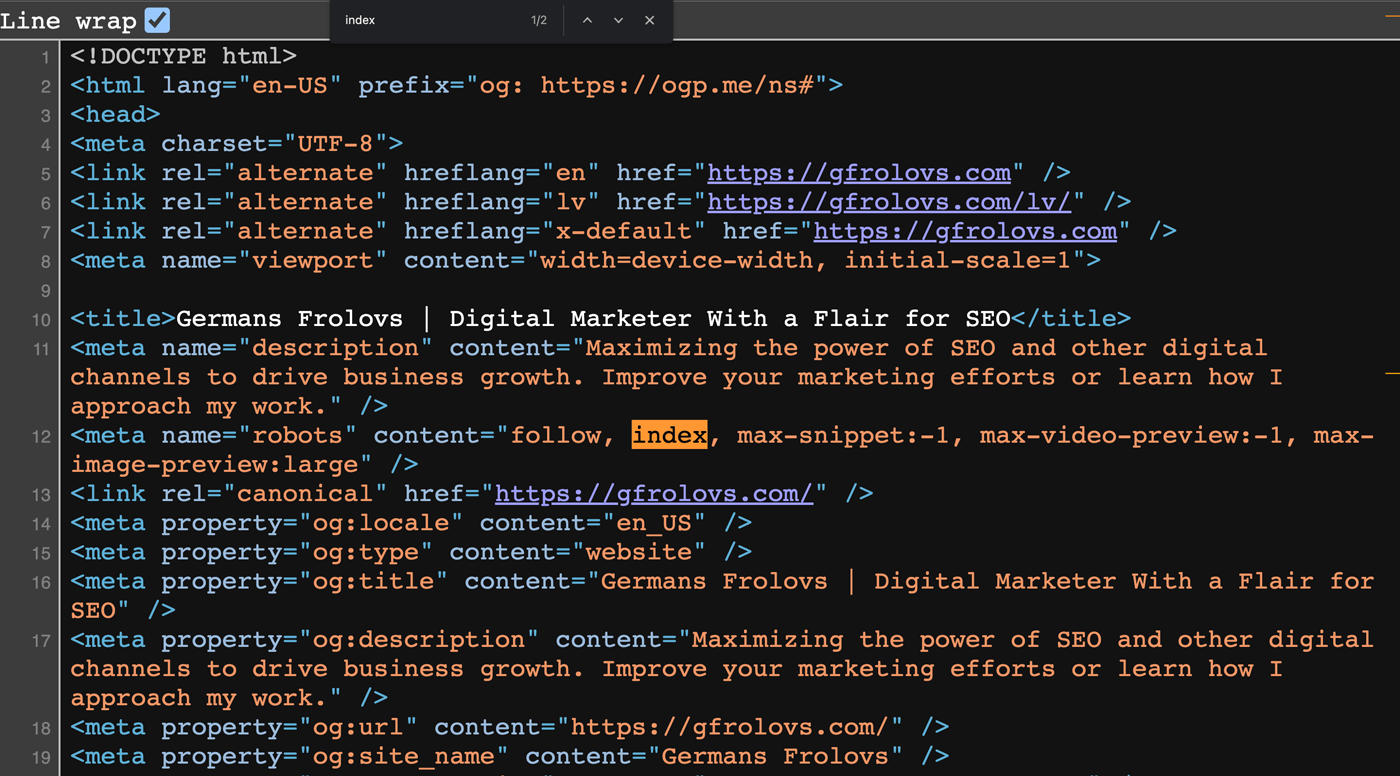
To show up on the SERPs, you would want those pages to be indexable.
In some cases, you may want specific pages not to appear in the search results for example some of your Pay-Per-Click (PPC) landing pages, your “Thank You for Subscribing” pages, or “Download the Resource Here” pages in the case of a lead magnet.
Another common reason why a page may not be indexed is due to very similar content on multiple pages without a proper canonical tag implementation.
Search engines like Google would pick one of the versions to index, and show it in the results. The other pages would not be indexed and therefore not appear.
Using canonical tags is a way to hint to search engines regarding which version of a page you’d like them to prioritize when they come across similar content on multiple pages.
The tag is placed within the <head> section of a duplicate page and looks like this:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/page-you-want-indexed/" />Other reasons why a page may not be indexed are duplicate content, low-quality content (i.e. content that is too short and/or does not provide any real value), redirections, or other technical issues.
What is Accessibility?
Accessibility refers to the ability of both search engine bots and users to easily access and interact with a webpage. It encompasses various aspects that ensure a website is usable, understandable, and perceivable by a diverse range of users, including those with disabilities or impairments.
There are several topics related to accessibility:
- Server performance: A slow or unreliable server that is not capable of handling the expected traffic can result in poor accessibility.
- HTTP status: The HTTP status codes returned by the server provide information about the accessibility and availability of webpages. For example, a “200 OK” status indicates that a page is accessible, while a “404 Not Found” status indicates that the page is inaccessible.
- Load time and page size: The speed at which webpage loads and the size of its resources (such as CSS, JavaScript, and images) affect accessibility.
- JavaScript rendering: Many modern websites rely heavily on JavaScript for interactive elements and dynamic content. However, search engine bots may not process JavaScript as effectively, potentially resulting in accessibility issues.
- Site architecture and page depth: Excessive page depth or orphan pages (pages with no internal links) can make it difficult for both users and search engine bots to navigate and access the content.
- Redirect chains: Redirect chains can delay the accessibility of pages, especially for slow-loading websites. The longer a chain of redirects is, the more time it takes for bots and users to reach their desired page.
What is Rankability?
Rankability refers to the ability of a webpage to achieve higher positions in search engine rankings.
Here are a couple of ways to boost rankability:
- Internal and external links: Links play a crucial role in enhancing rankability. Internal links can improve crawl rate, guide users and search engine bots towards related pages, and increase the ability to rank higher. External links derived from off-page SEO optimization efforts can also improve rankings significantly.
- Content optimization: Creating high-quality SEO content and interlinking topically related pages helps to establish topical coverage. By focusing on specific topics and incorporating related concepts, these content networks help improve the page’s relevance and ranking potential.
What is Clickability?
Clickability refers to the ability of a webpage to attract user clicks in search engine result pages (SERPs).
It mostly involves optimizing on-page SEO and technical elements to enhance the appearance and appeal of the webpage’s listing, increasing the likelihood of user engagement.
Here are some areas to focus on when optimizing for clickability:
- Content structure: Organizing your content using clear structures like lists, tables, and headings helps search engines understand the information better. This can result in the generation of featured snippets and other visually enhanced results that stand out in the SERPs.
- Structured data markup: Implementing structured data using Schema.org markup provides additional information to search engines, enriching your URL listings in the SERPs. This can include breadcrumbs, star ratings, product information, event details, recipe details, site links, and more.
- Visual content optimization: Utilizing videos and images with appropriate markup gives you an advantage in image and video search results.
What Technical SEO Best Practices Should You Follow?
Now that you have an understanding of the technical aspects of SEO, here are some best practices to follow.
Create SEO-Friendly Site Structure
Site structure, also known as site architecture, is the organization of your pages in a hierarchy that makes sense to both users and search engine bots.
Effective site structure lets bots crawl your website more efficiently and discover new content faster.
A best practice is to ensure that all the important pages are accessible in up to three clicks and make sure that pages are not grouped too deeply.
A site structure example for an eCommerce store selling protein supplements is illustrated below.
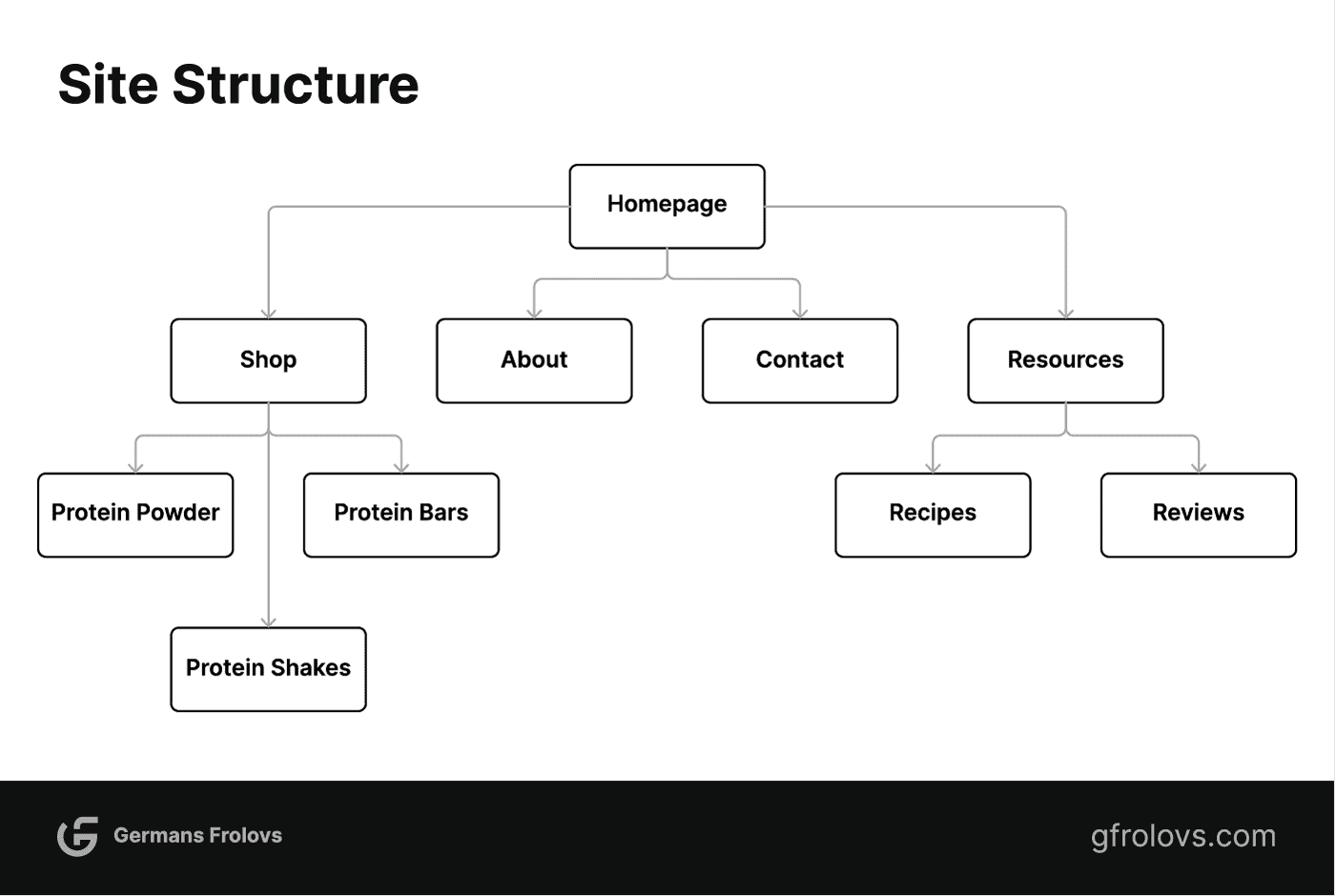
Pages are structured in a hierarchy with the home page being the top level. Following that, levels can be organized based on topic or category pages and then individual pages.
Submit Your Sitemap
Sitemaps are lists of URLs on your site that inform search engines about the pages available.
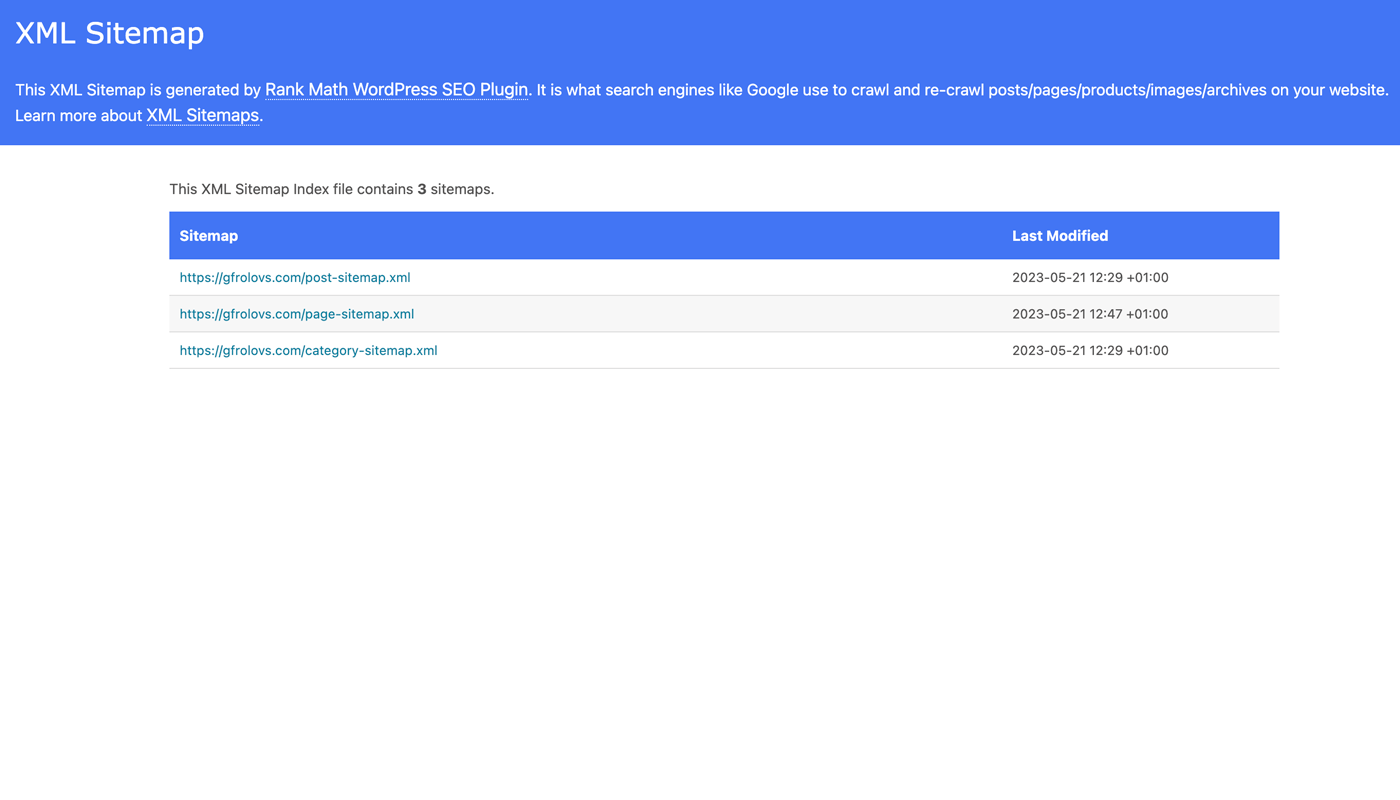
Submitting a sitemap helps ensure that all the pages are discovered and indexed.
To create a sitemap, you can use various free online tools or SEO plugins that generate a list of URLs on your website.
You can then submit your sitemap directly to Google Search Console or other search engine webmaster tools.
To submit directly to Google Search Console, you will need to first locate your sitemap.xml file.
Then copy the URL (i.e., https://example.com/sitemap.xml).
Go to Google Search Console > Indexing > Sitemaps.
Find the “Add a new sitemap” field, and paste the URL.
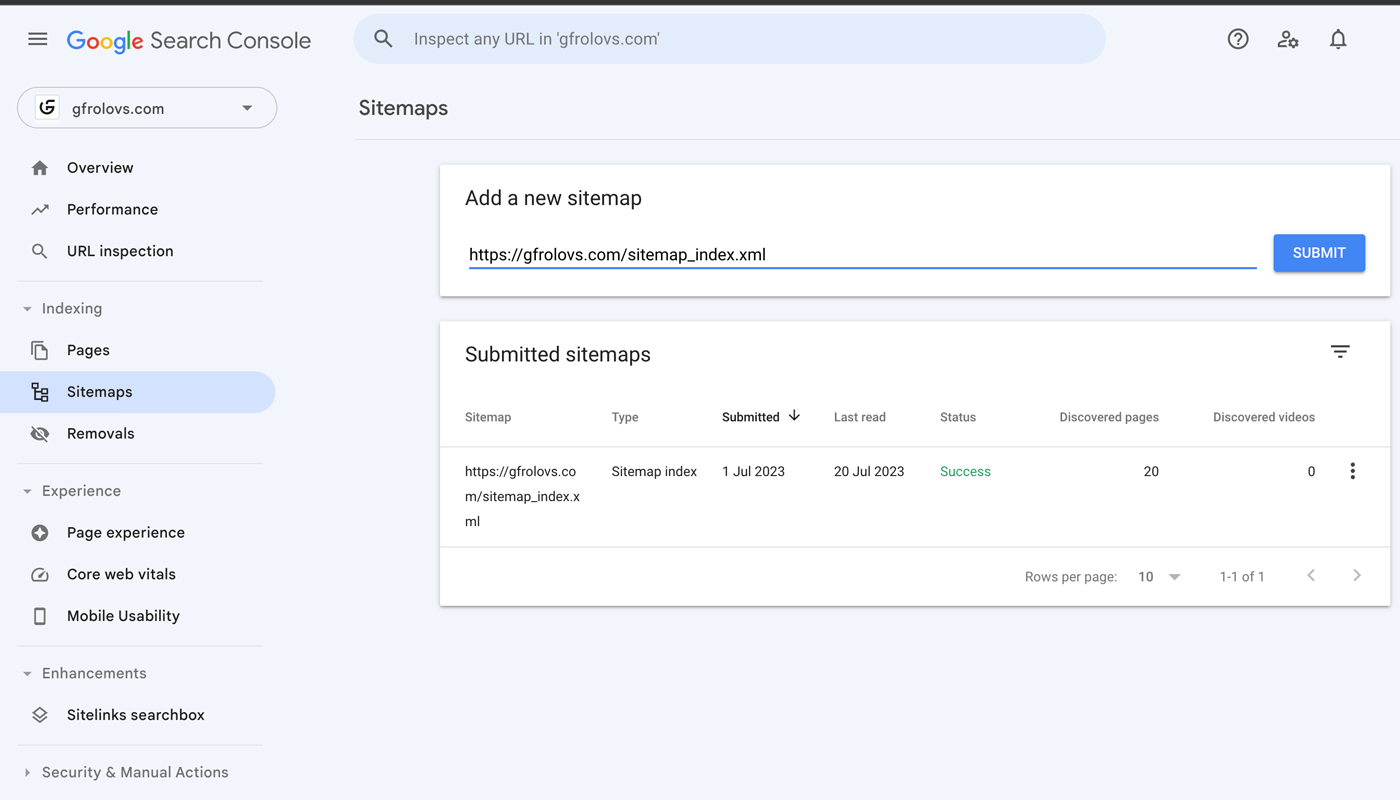
Click “Submit” and your sitemap will be submitted to Google.
Utilize Robots.txt
As mentioned above, robots.txt is a text file used to control how search engine bots crawl your website.
It is important to ensure that the robots.txt file is configured correctly so that you are not blocking any important content or allowing bots to crawl pages that should not be crawled.
You can find a robots.txt file in the root directory of your website, i.e., “https://example.com/robots.txt”.
Most CMS (Content Management Systems) provide a default robots.txt, but it is important to review and customize the file according to your requirements.
Use HTTPS
HTTPS is a secure version of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and provides data encryption during transfer.
HTTPS has been a ranking factor since 2014 and it is important to switch to a secure connection for all of your website’s pages.
It is recommended to use a reliable SSL certificate, such as Let’s Encrypt, to ensure that the connection between your website and users’ browsers is encrypted.
Most web hosting providers offer free SSL certificates these days.
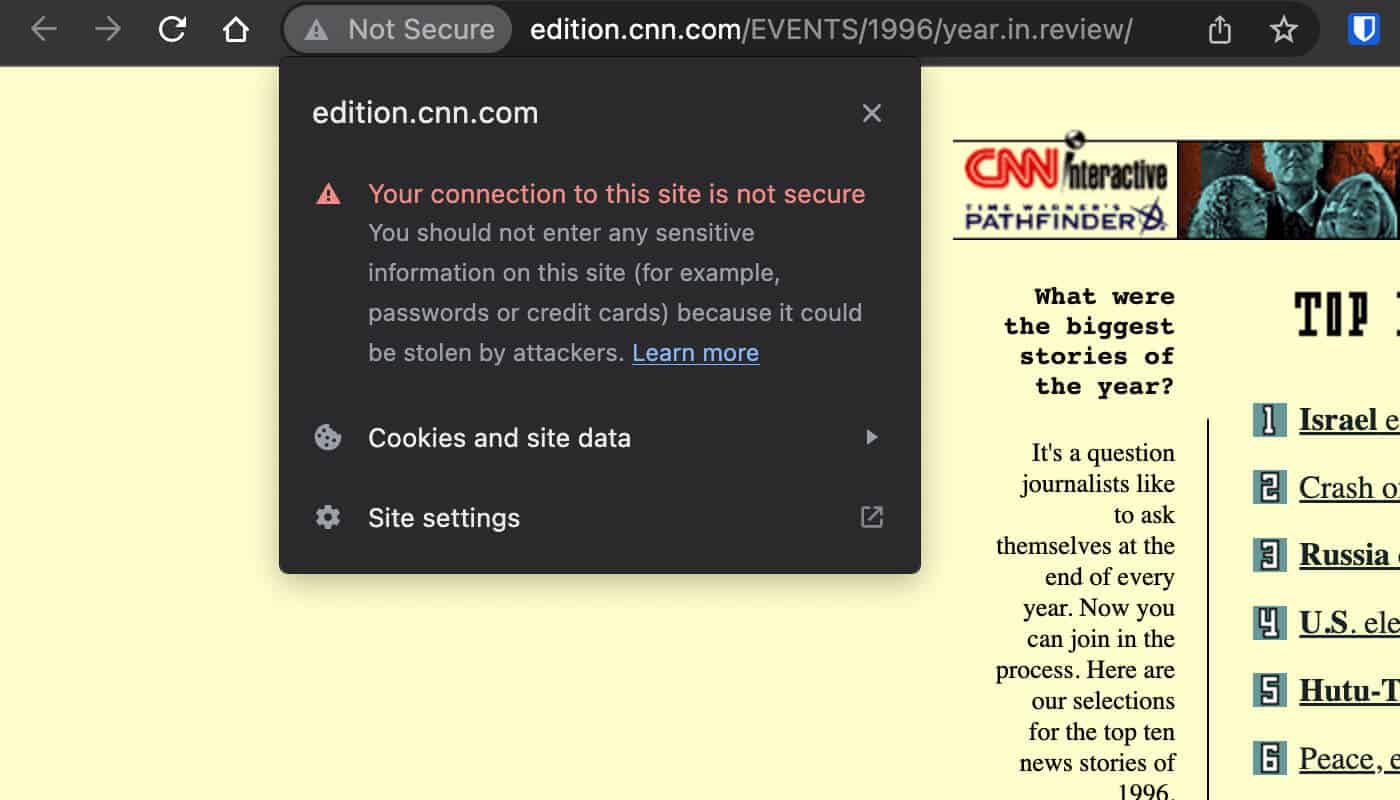
To check if a website is using HTTPS, look for the padlock icon next to the URL in the browser bar.
If you see the “Not Secure” warning, it means that the website is not using HTTPS.
Improve Your Page Speed
Page speed is the time it takes for a page to load and is a minor ranking factor.
So, you should ensure pages on your site load as fast as possible but never prioritize that over content quality.
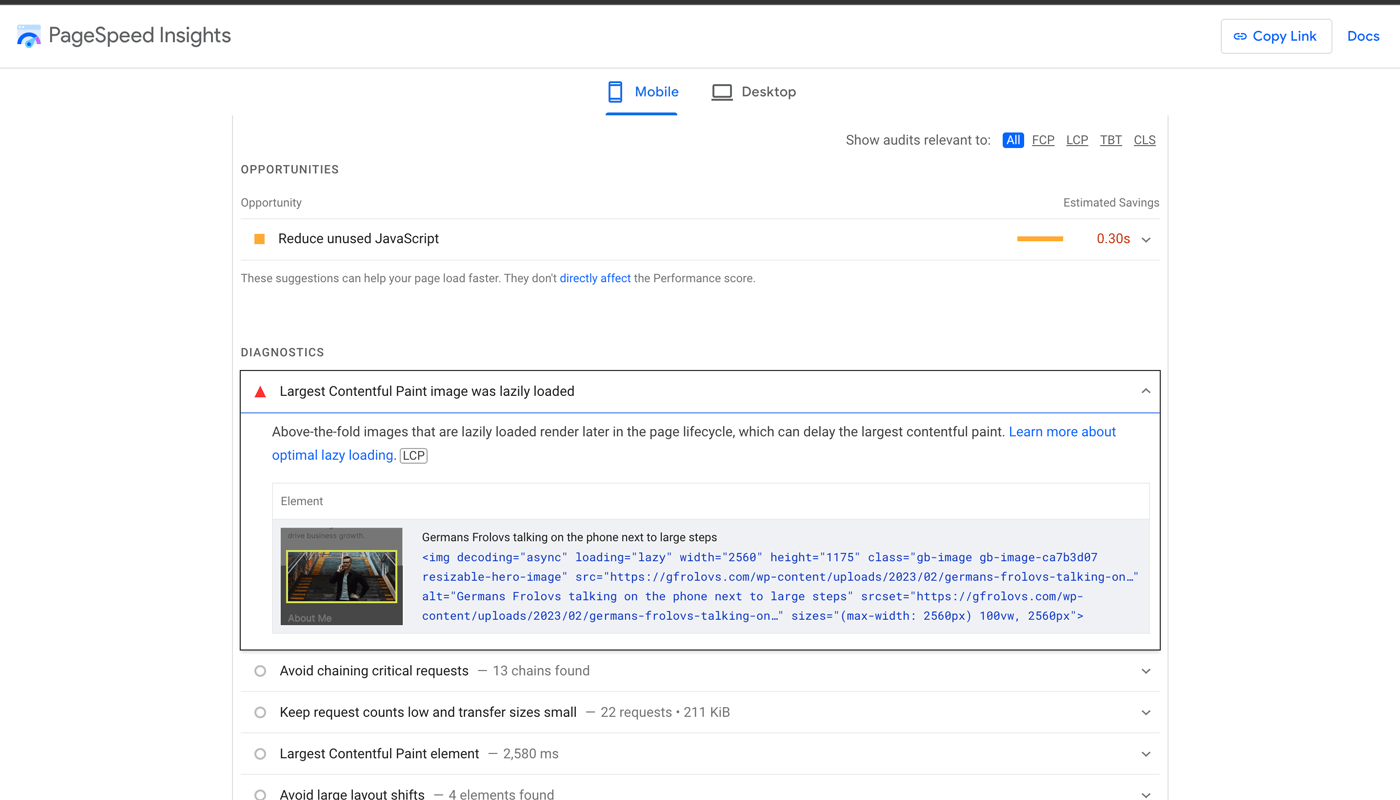
You can use Google PageSpeed Insights to identify the issues that are impacting your website speed.
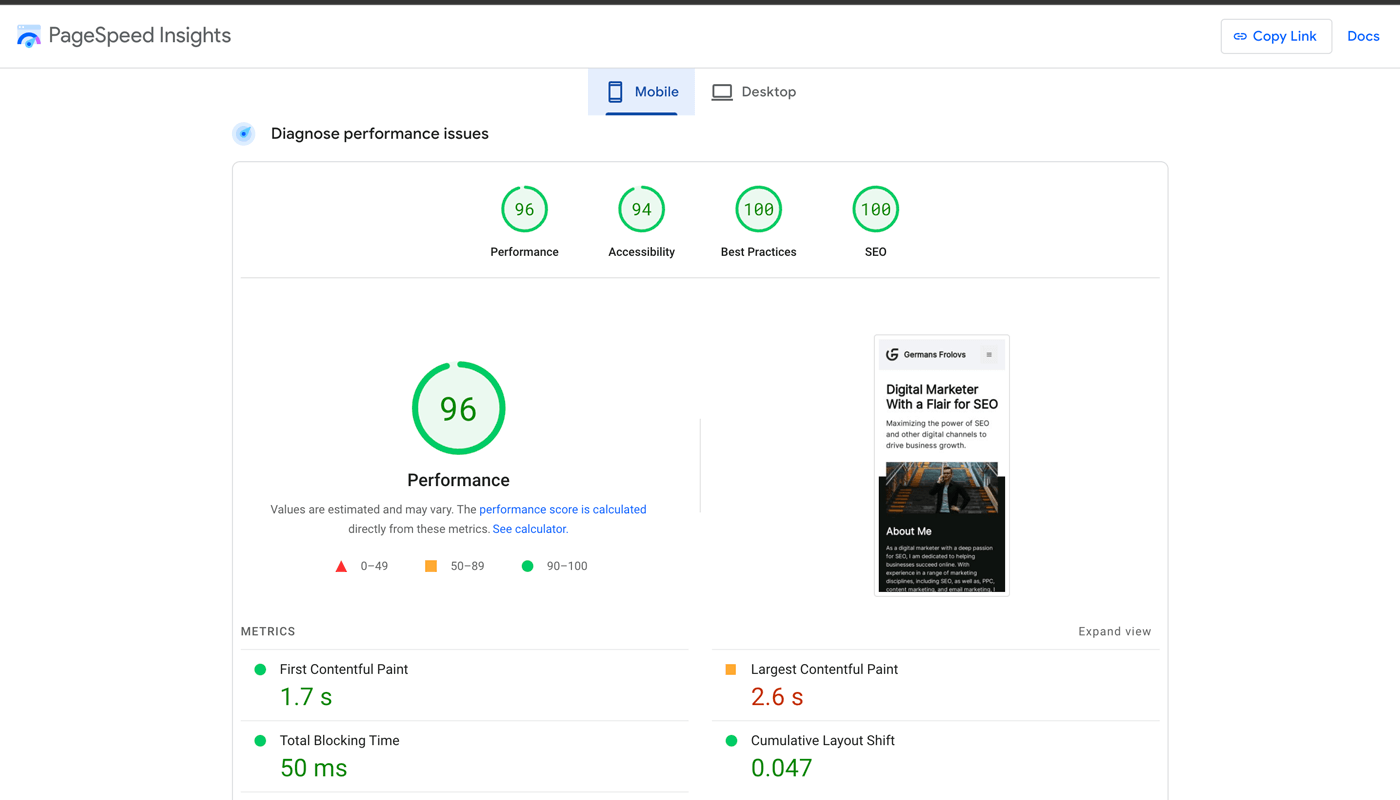
Then use the recommendations provided to fix the issues.
Here are some best practices for improving page speed:
- Minify HTML, CSS, and Javascript files: Minification helps reduce the size of the files by removing unnecessary characters (e.g., white spaces, line breaks) in the code, thereby enabling the page to load faster.
- Optimize images: Compressing images and optimizing image sizes reduces their file size and improves page loading time.
- Enable browser caching: This helps store static content (e.g., HTML, CSS, Javascript) in the user’s browser so that it does not have to be reloaded each time they visit your website.
- Use CDN (Content Delivery Network): CDN stores your static content in multiple servers located around the world so that users can access the content quickly from a server nearest to them.
Optimize for Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are three essential metrics for measuring user experience (UX) and they became a minor ranking factor in 2021.
The core web vitals include:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the loading performance of the page.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity of a page.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability of a page.
Note that the First Input Delay (FID) metric will be replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP) in March 2024.
Google has established specific thresholds for each Core Web Vital, categorizing them as “Good,” “Needs Improvement,” or “Poor,” which aids in assessing their performance quality.
You can use Google PageSpeed Insights to measure your website’s Core Web Vitals and make improvements accordingly.
Ensure Your Website Is Mobile-Friendly
Your website should be optimized for mobile devices as most of the online searches are conducted from smartphones.
Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool can help you assess how well your website is optimized for mobile users.
If the test fails, it will provide actionable insights into what changes to make to ensure a better user experience on mobile devices.
Find & Fix Broken Pages
Broken pages (404 errors) can negatively affect the user experience, which is why it’s important to identify and fix them as soon as possible.
You can use tools such as Ahrefs’s Site Audit Tool, Google Search Console, or Screaming Frog SEO Spider Website Crawler to find broken pages on your website.
Once you have identified the broken pages, make sure they are either:
- Redirected appropriately
- Removed from your website permanently (using 410 status code)
- Restored in case of accidental deletion
Find & Fix Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content includes pages with exact or near duplicate content on multiple pages on your site.
It’s important to identify and address duplicate content issues because having multiple pages with the same content can bring various issues:
- Wrong page ranking in search results
- The page is not being indexed
- Backlinks value being wasted
- Wasted crawl budget
You can find duplicate content on your site using Ahrefs Site Audit or Ahrefs Webmaster Tools, Screaming Frog SEO Spider Website Crawler, or Siteliner.
To fix the issue, you can follow any of the methods mentioned below:
- Remove the duplicate page
- Add a canonical tag to provide a hint to search engines about the preferred version of the page
- Use a 301 redirect from a duplicate page to another relevant page
- Provide more context and unique content to the duplicate page to differentiate it from the other page(s)
- Consolidate duplicate content into a single page
Find & Fix Redirect Chains
Redirect chains are when multiple redirects happen in a row (e.g., URL A redirects to B which then redirects to C).
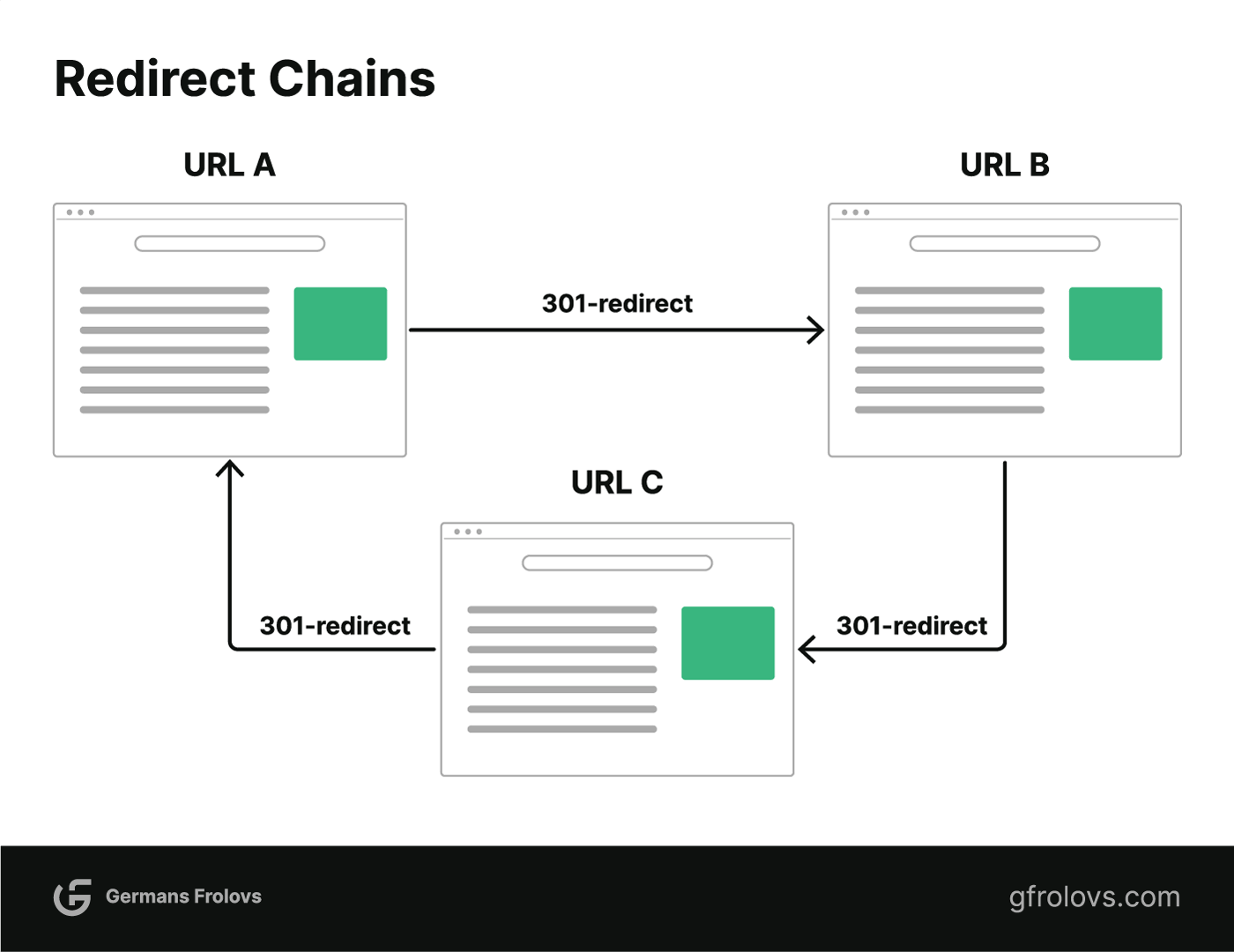
This can affect page speed as the browser needs to make multiple requests for the final page.
To identify redirect chains, you can use tools such as Screaming Frog SEO Spider Website Crawler and Ahrefs Site Audit Tool.
To fix a redirect chain, you need to remove or update any unnecessary or outdated redirects so that the URL redirection occurs directly without passing through multiple intermediate redirects.
Implement Structured Data
Structured data helps search engines understand the content on your website better and can enhance how it appears in their search results.
You can use structured data (Schema) to let search engines know about the type of content, its properties, and other information. This helps them display more information about your website when it appears in their search results increasing clickability.
Google supports various types of structured data, such as Articles, Events, Reviews, and more.
For example, you run an events business and you have an upcoming event. You can add an Events schema to your page which will enable Google to display the date, time, and other details of the event in its search results.
There are various tools available for implementing Schema Markup on websites. One I recommend the most is Merkle’s Schema Markup Generator (JSON-LD).
Use Hreflang for Multiple Languages
If you have a multilingual website, then it’s important to use hreflang tags.
Hreflang tags provide search engines with information on which language versions of your page are available and help them decide which version is most relevant for users searching in different languages or regions.
For example, the homepage of my website is available in both English and Latvian languages.
Here is my site’s homepage in English.
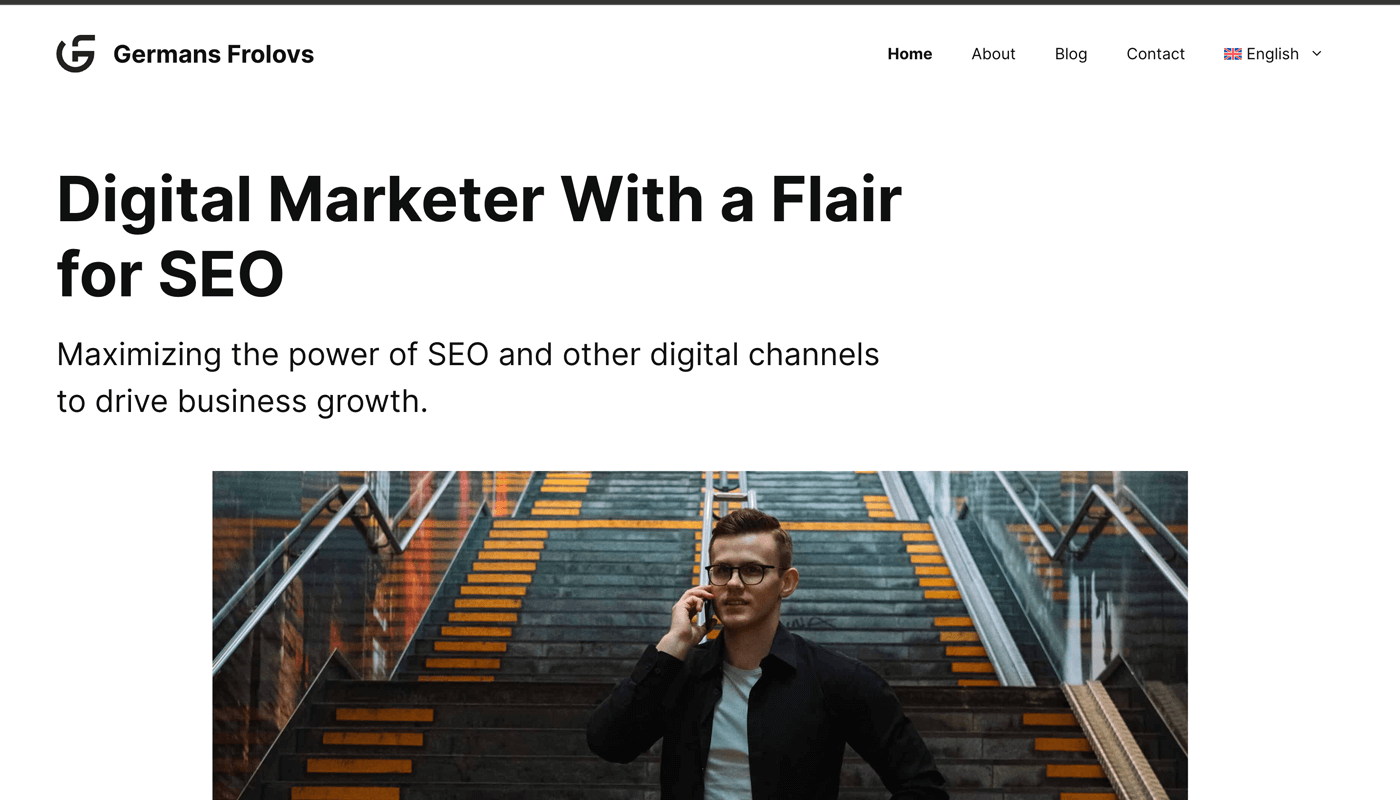
And here’s the same page in Latvian.

Each of these pages has corresponding hreflang tags in the <head> section of all versions of the page.
For example, you would need to add the following hreflang tags if you have your homepage in English and Latvian, and have a “.com” generic top-level domain (just like I do on my site):
<head>
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://example.com" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="lv" href="https://example.com/lv/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://example.com" />
</head>Regularly Monitor Technical SEO Issues
It’s important to regularly monitor your website for any technical SEO issues, such as broken pages, duplicate content, or server errors.
To get started, you can use Google Search Console to monitor issues with your website.
You can also use tools such as Ahrefs Site Audit or Screaming Frog SEO Spider Website Crawler to scan your entire website for technical SEO issues and get actionable insights on how to fix them.
And in case you do not know how to fix a particular issue you can always search for it on Google.
What Tools Could Help With Technical SEO?
There are various free SEO tools available that can help you get started with technical SEO:
- Google Search Console: Helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your website’s presence in Google’s search results. The tool offers insights into your site’s performance, indexing status, and any issues that need to be addressed.
- Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test: Analyzes your website and determines whether it is mobile-friendly. With the increasing number of mobile users, this tool is essential for ensuring a good user experience on all devices.
- Google’s PageSpeed Insights: Analyzes your website’s speed and user experience, and offers suggestions for improvements.
- Google Chrome DevTools: This suite of web development and debugging tools built into the Google Chrome browser allows you to diagnose and fix technical SEO issues such as rendering problems, slow page load times, and more.
- Ahrefs’ SEO Toolbar: This free browser extension provides useful data for any web page you visit, enabling you to quickly check broken links, redirects, hreflang tags, and more.
- Ahrefs’ Site Audit Tool: This powerful crawler analyzes your entire website to detect technical SEO issues, prioritize them by importance, and offer actionable recommendations to help you fix them.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider Website Crawler: This desktop program crawls your website to identify and report SEO issues such as broken links, duplicate content, missing metadata, slow page load times, and more.
Check out this list of the best free SEO tools to explore a range of free tools that can help optimize your website, whether you need assistance with technical SEO, on-page optimization, or off-page strategies.